Dynamic Changes of Regulatory T Cells/CD4⁺ T Cells in Peripheral Blood of Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Comparison of Pediatric and Adult Kidney Donors
- PMID: 37749867
- PMCID: PMC10541792
- DOI: 10.12659/AOT.940604
Dynamic Changes of Regulatory T Cells/CD4⁺ T Cells in Peripheral Blood of Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Comparison of Pediatric and Adult Kidney Donors
Abstract
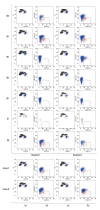
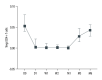
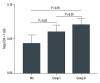
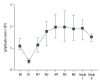
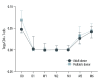
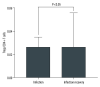
BACKGROUND Inducing transplantation tolerance and monitoring the recipient's immune status to improve allograft survival remains the main goal for kidney transplantation (KTx). MATERIAL AND METHODS A total of 53 renal transplantation patients and 20 healthy individuals were assigned to the post-transplantation and healthy groups, respectively; 10 recipients with stable renal function for 2 years after kidney transplantation were assigned to Group C. Eleven kidney transplantation recipients were hospitalized due to lung infection. Flow cytometry was used to measure levels of Tregs/CD4⁺ T cells. RESULTS The Tregs/CD4⁺ T cells ratio reached homeostasis 6 months after KTx, with no significant difference between Group D (healthy control group) and pre-surgery or Group C (2 years after KTx group). The pediatric donor group and the adult donor group reached immune homeostasis 3 months after the operation. Immune homeostasis is maintaining a balance between immune tolerance and immunogenicity. There was no significant difference in graft function between the pediatric and adult donor groups before surgery, 1 day after surgery, 1 week after surgery, 2 weeks after surgery, and 1 month after surgery; however, graft function was significantly better in the pediatric donor group compared with the adult donor group at 3 mouths (eGFR: 51.7 (40.4-66.2) vs 73.0 (55.7-90.2), P=0.008<0.05) and 6 months (eGFR: 52.2 (37.5-62.8) vs 80.5 (64.1-90.4), P<0.001) after surgery. Pediatric donor kidneys reached immune homeostasis 3 months after surgery, with better graft function at this time compared with adult donor kidneys. The proportion of Tregs/CD4⁺ T cells in recipients with a pulmonary infection after KTx was lower than in those with infection recovery. CONCLUSIONS Expanding the use of pediatric kidneys should be further explored by the transplantation community. The proportion of Tregs/CD4⁺ T cells in recipients with a pulmonary infection after KTx was lower than in those with infection recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of regulatory T cells on short-term graft outcome in kidney transplant recipients, a prospective observational, single-center study.Transpl Immunol. 2022 Aug;73:101630. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101630. Epub 2022 May 25. Transpl Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35643376
-
Excellent clinical outcomes of renal transplant from pediatric deceased donors with acute kidney injury.Eur J Med Res. 2023 May 4;28(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01111-9. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37143170 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Transplant Outcome Is Associated with Regulatory T Cell Population and Gene Expression Early after Transplantation.J Immunol Res. 2019 Jan 8;2019:7452019. doi: 10.1155/2019/7452019. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30729139 Free PMC article.
-
CD45RA-CD25highCD127-CD4+ activated regulatory T cells are correlated with de novo donor-specific anti-HLA antibody formation after kidney transplantation in standard immunosuppression.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Aug;97:107661. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107661. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33887579
-
Accumulation of High Levels of Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Enhances Graft Survival in Almost-Tolerant Kidney Transplant Recipients.Transplant Proc. 2018 Dec;50(10):3314-3320. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.04.043. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Transplant Proc. 2018. PMID: 30577201
References
-
- Krämer BK, Zülke C, Kammerl MC, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors and estimated risk for CAD in a randomized trial comparing calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003;3(8):982–87. - PubMed
-
- Naesens M, Kuypers DR, Sarwal M. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(2):481–508. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum LM, Lipman M, Paraskevas S, et al. Management of chronic allograft nephropathy: A systematic review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(4):860–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

