Gallic Acid Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment Caused by Sleep Deprivation through Antioxidant Effect
- PMID: 37749929
- PMCID: PMC10569142
- DOI: 10.5607/en23015
Gallic Acid Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment Caused by Sleep Deprivation through Antioxidant Effect
Abstract
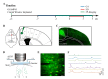
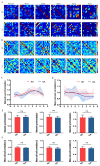
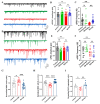
Sleep deprivation (SD) has a profound impact on the central nervous system, resulting in an array of mood disorders, including depression and anxiety. Despite this, the dynamic alterations in neuronal activity during sleep deprivation have not been extensively investigated. While some researchers propose that sleep deprivation diminishes neuronal activity, thereby leading to depression. Others argue that short-term sleep deprivation enhances neuronal activity and dendritic spine density, potentially yielding antidepressant effects. In this study, a two-photon microscope was utilized to examine the calcium transients of anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) neurons in awake SD mice in vivo at 24-hour intervals. It was observed that SD reduced the frequency and amplitude of Ca2+ transients while increasing the proportions of inactive neurons. Following the cessation of sleep deprivation, neuronal calcium transients demonstrated a gradual recovery. Moreover, whole-cell patch-clamp recordings revealed a significant decrease in the frequency of spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic current (sEPSC) after SD. The investigation also assessed several oxidative stress parameters, finding that sleep deprivation substantially elevated the level of malondialdehyde (MDA), while simultaneously decreasing the expression of Nuclear Factor erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) and activities of Superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the ACC. Importantly, the administration of gallic acid (GA) notably mitigated the decline of calcium transients in ACC neurons. GA was also shown to alleviate oxidative stress in the brain and improve cognitive impairment caused by sleep deprivation. These findings indicate that the calcium transients of ACC neurons experience a continuous decline during sleep deprivation, a process that is reversible. GA may serve as a potential candidate agent for the prevention and treatment of cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation.
Keywords: ACC; Gallic acid; Oxidative stress; Sleep deprivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

