A Survey of Conversational Agents and Their Applications for Self-Management of Chronic Conditions
- PMID: 37750107
- PMCID: PMC10519706
- DOI: 10.1109/COMPSAC57700.2023.00162
A Survey of Conversational Agents and Their Applications for Self-Management of Chronic Conditions
Abstract
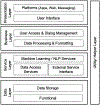
Conversational agents have gained their ground in our daily life and various domains including healthcare. Chronic condition self-management is one of the promising healthcare areas in which conversational agents demonstrate significant potential to contribute to alleviating healthcare burdens from chronic conditions. This survey paper introduces and outlines types of conversational agents, their generic architecture and workflow, the implemented technologies, and their application to chronic condition self-management.
Keywords: Conversational agents; chronic conditions; intelligent agents architecture; self-management.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “About Chronic Diseases.” https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/index.htm (accessed Mar. 27 2023).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “Chronic Diseases in America.” https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/infographic/chronic-disease... (accessed Mar. 27 2023).
-
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, “National diabetes statistics report, 2017,” CS279910-A, 2017. (accessed Mar. 27 2023).
-
- Rijken M, Jones M, Heijmans M, and Dixon A, “Supporting self-management,” in Caring for People with Chronic Conditions. A Health System Perspective., Nolte E and McKee M, Eds. Berkshire, UK: Open University Press, 2008, pp. 116–142.
-
- Barlow J, Wright C, Sheasby J, Turner A, and Hainsworth J, “Self-management approaches for people with chronic conditions: a review,” Patient Educ. Couns, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 177–187, 2002. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources