In vivo comparison of implantation behavior and laboratory analysis of two preloaded intraocular lens injectors
- PMID: 37750504
- PMCID: PMC11082425
- DOI: 10.1177/11206721231204382
In vivo comparison of implantation behavior and laboratory analysis of two preloaded intraocular lens injectors
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated implantation behavior and injector damage of two different IOL injector systems, the Multisert and the AutonoMe.
Design: Prospective, randomized, comparative study with laboratory investigation.
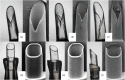
Methods: We examined used injectors from 48 bilateral cataract cases and assessed video recordings of each Implantation. All eyes were intraindividually randomized for treatment with one of the two IOL injectors. Implantation videos were reviewed for inadvertent events and the time for different implantation steps was determined. The injector nozzle tips were examined using light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Damage was graded using the Heidelberg Score for IOL injector damage (HeiScore). Three months postoperatively, IOLs were assessed for material changes.
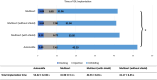
Results: Implantation was without critical events in 96 of 96 eyes. Mean implantation time was 41.90 ± 7.11 s with the Multisert and 52.22 ± 12.06 s with the AutonoMe. In the AutonoMe group, we observed 4 eyes (8.3%) with a failed docking attempt, 28 eyes (58.3%) with a haptic adherence, one case (2.1%) of straight leading haptic and 2 cases (4.2%) of intrawound IOL manipulation. There were no events observed in the Multisert group. The mean HeiScore values were 0.87 ± 0.61 and 3.68 ± 0.47 for the AutonoMe and Multisert. 3 months postoperatively, IOL material changes were absent.
Conclusions: Both injectors allowed safe and controlled implantation. Using Multisert, implantation behavior was more consistent. The injectors showed different damage profiles with a higher damage score for the Multisert.The study is registered at the German Clinical Trials Register (Deutsches Register Klinischer Studien; reference number: DRKS00007837).
Keywords: IOLs < LENS / CATARACT; LENS / CATARACT; Surgical instruments / special techniques < LENS / CATARACT; clinical tests < LENS / CATARACT; intraoperative complications of cataract surgery < LENS / CATARACT.
Figures


References
-
- Borkenstein AF, Borkenstein E-M. Safety first-evaluation of IOL injector systems. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 2019; 236(8): 976–982. - PubMed
-
- Cennamo M, Favuzza E, Salvatici MC, et al. Effect of manual, preloaded, and automated preloaded injectors on corneal incision architecture after IOL implantation. Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery 2020; 46(10): 1374–1380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

