The DBL-1/TGF-β signaling pathway tailors behavioral and molecular host responses to a variety of bacteria in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 37750680
- PMCID: PMC10567113
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75831
The DBL-1/TGF-β signaling pathway tailors behavioral and molecular host responses to a variety of bacteria in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
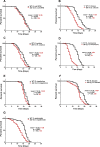
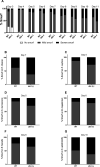
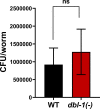
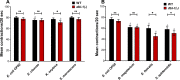
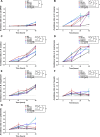
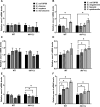
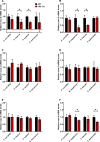
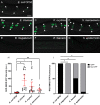
Generating specific, robust protective responses to different bacteria is vital for animal survival. Here, we address the role of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) member DBL-1 in regulating signature host defense responses in Caenorhabditis elegans to human opportunistic Gram-negative and Gram-positive pathogens. Canonical DBL-1 signaling is required to suppress avoidance behavior in response to Gram-negative, but not Gram-positive bacteria. We propose that in the absence of DBL-1, animals perceive some bacteria as more harmful. Animals activate DBL-1 pathway activity in response to Gram-negative bacteria and strongly repress it in response to select Gram-positive bacteria, demonstrating bacteria-responsive regulation of DBL-1 signaling. DBL-1 signaling differentially regulates expression of target innate immunity genes depending on the bacterial exposure. These findings highlight a central role for TGF-β in tailoring a suite of bacteria-specific host defenses.
Keywords: C. elegans; Smad; TGF-β; dbl-1; genetics; genomics; host response; innate immunity.
© 2023, Madhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
BM, ML, TG No competing interests declared
Figures
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2021.03.30.437693
References
-
- Ahamefule CS, Qin Q, Odiba AS, Li S, Moneke AN, Ogbonna JC, Jin C, Wang B, Fang W. Caenorhabditis elegans-based Aspergillus fumigatus infection model for evaluating pathogenicity and drug efficacy. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2020;10:320. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

