Five-year Maintenance of Clinical Response and Consistent Safety Profile for Guselkumab in Asian patients with Psoriasis from VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2
- PMID: 37750995
- PMCID: PMC10613179
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-023-01026-7
Five-year Maintenance of Clinical Response and Consistent Safety Profile for Guselkumab in Asian patients with Psoriasis from VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2
Abstract
Introduction: Guselkumab is a human monoclonal antibody against IL-23 used in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. This post-hoc analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in the Asian subpopulation of VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 through 5 years.
Methods: The proportions of guselkumab-treated Asian patients (VOYAGE 1 and 2) achieving Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 and PASI 100, Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) scores of 0/1 and 0, and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores of 0/1 (week 100 through week 252) were assessed. Non-responders were patients who met the treatment failure rules. Efficacy endpoints were analyzed using the as-observed methodology (no missing data imputation) for both studies and using non-responder imputation (for patients with any missing data) in VOYAGE 1. Safety outcomes were based on pooled data through week 252.
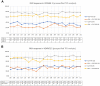
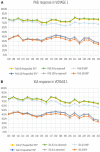
Results: Response rates through week 252 for 199 Asian patients in the guselkumab group in VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2, respectively, were 76.8% and 80.6% (PASI 90), 26.8% and 38.7% (PASI 100), 64.3% and 87.1% (IGA 0/1), and 26.8% and 45.2% (IGA 0). DLQI (0/1) at week 252 was achieved by 52.7% of patients in VOYAGE 1 and 61.3% in VOYAGE 2, while DLQI (0) at week 252 was achieved by 32.7% of patients in VOYAGE 1 and 40.3% in VOYAGE 2. The safety profile was similar to the global population and remained consistent through 5 years. Asian patients were followed for a total of 814 patient-years (PY). Over 85% of the guselkumab-treated patients continued treatment through week 264. The rate of serious adverse events (AEs) at week 252 was 3.07/100 PY. Rates of AEs of interest were low: serious infections, 0.74/100 PY; nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), no patients; malignancies other than NMSC, 0.12/100 PY; and no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Conclusion: These analyses confirm a continuous response over 5 years, indicating that guselkumab shows therapeutic longevity in Asian patients requiring long-term treatment for moderate-to-severe psoriasis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers: VOYAGE 1 [NCT02207231] and VOYAGE 2 [NCT02207244].
Keywords: Asian; Biologics; Guselkumab; Moderate-to-severe; Psoriasis.
Plain language summary
Psoriasis—a long-term condition that causes a skin rash with scaly, itchy patches (plaques)—is becoming more prevalent in Asia. To control symptoms of moderate-to-severe psoriasis and achieve a strong improvement in the patient’s quality of life, continuous treatment is usually needed. Guselkumab is a medicine that targets specific parts of the immune system to treat moderate-to-severe psoriasis. It is important to understand the long-term benefits of guselkumab in Asian patient populations. Our study analyzed the data from two randomized clinical trials (called VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2) that studied people with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. We examined results for the 199 people from Asia, including Korea and Taiwan, who took part in these studies. Overall, 162 of the 184 (86.6%) people from Asia treated with guselkumab incorporated into these studies continued the treatment for 5 years. Patients treated with guselkumab showed effective clinical responses (improvements measured by clinicians), including high skin clearance, meaning a large reduction in skin surface area affected by psoriasis. On guselkumab, patients also reported improvements in their skin-related health-related quality of life. These improvements and the efficacy of guselkumab were maintained over 5 years of follow-up. The safety results for guselkumab in the Asian subpopulation were similar to those for the global population, showing low rates of serious adverse effects, as expected from this type of medicine. Overall, our study found a favorable benefit–risk profile with continuous guselkumab treatment for 5 years in Asian people with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. This highlights that guselkumab treatment allows long-lasting control of this disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Byung Soo Kim has served as a scientific adviser, a clinical study investigator and/or a speaker for AbbVie, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Regeneron, Samsung, Sanofi and UCB. Seong-Jin Jo has conducted clinical trials for, acted as a consultant for, or received speaker’s honoraria from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daewoong, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi. SangWoong Youn served as a speaker for AbbVie, Cellgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis and Pfizer organised psoriasis symposium or meetings, and has also performed phase III clinical trials sponsored by Janssen, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin and UCB and phase IV clinical trials sponsored by CKD Pharma, Janssen and LEO Pharma. Kristian Reich has served as a paid advisor and/or a paid speaker for and/or participated in clinical trials (site received patient fees, received fees if acting as a coordinating investigator) sponsored by AbbVie, Affibody, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen-Idec, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Celgene, Covagen, Forward Pharma, Fresenius Medical Care, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Janssen-Cilag, Kyowa Kirin, Leo, Eli Lilly, Medac, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Miltenyi, Novartis, Ocean Pharma, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Takeda, UCB Pharma, Valeant and Xenoport. Carine Saadoun, Chia-Ling Chang and Ya-Wen Yang are employees of Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson. Yu-Huei Huang has conducted clinical trials while serving as a principal investigator for AbbVie, Galderma, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag Pharmaceutica, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Pfizer and has received honoraria for serving as an advisory board member for and speaking fees from AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag Pharmaceutica, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Pfizer Limited. Tsen-Fang Tsai has conducted clinical trials or received honoraria for serving as a consultant for Abbvie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli‐Lilly, Galderma, GSK, Janssen‐Cilag, Leo Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis International, Pfizer, PharmaEssentia, Sanofi, and UCB Pharma.
Figures

References
-
- Tsai TF, Ho JC, Song M, Szapary P, Guzzo C, Shen YK, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in Taiwanese and Korean patients (PEARL) J Dermatol Sci. 2011;63(3):154–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chiu HY, Wang TS, Chen PH, Hsu SH, Tsai YC, Tsai TF. Psoriasis in Taiwan: from epidemiology to new treatments. Dermatol Sin. 2018;36:115–123. doi: 10.1016/j.dsi.2018.06.001. - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

