Hyperphosphorylation of BCL-2 family proteins underlies functional resistance to venetoclax in lymphoid malignancies
- PMID: 37751299
- PMCID: PMC10645378
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI170169
Hyperphosphorylation of BCL-2 family proteins underlies functional resistance to venetoclax in lymphoid malignancies
Abstract
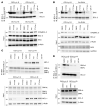
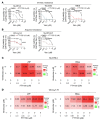
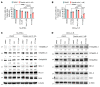
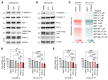
The B cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor venetoclax is effective in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); however, resistance may develop over time. Other lymphoid malignancies such as diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are frequently intrinsically resistant to venetoclax. Although genomic resistance mechanisms such as BCL2 mutations have been described, this probably only explains a subset of resistant cases. Using 2 complementary functional precision medicine techniques - BH3 profiling and high-throughput kinase activity mapping - we found that hyperphosphorylation of BCL-2 family proteins, including antiapoptotic myeloid leukemia 1 (MCL-1) and BCL-2 and proapoptotic BCL-2 agonist of cell death (BAD) and BCL-2 associated X, apoptosis regulator (BAX), underlies functional mechanisms of both intrinsic and acquired resistance to venetoclax in CLL and DLBCL. Additionally, we provide evidence that antiapoptotic BCL-2 family protein phosphorylation altered the apoptotic protein interactome, thereby changing the profile of functional dependence on these prosurvival proteins. Targeting BCL-2 family protein phosphorylation with phosphatase-activating drugs rewired these dependencies, thus restoring sensitivity to venetoclax in a panel of venetoclax-resistant lymphoid cell lines, a resistant mouse model, and in paired patient samples before venetoclax treatment and at the time of progression.
Keywords: Apoptosis survival pathways; Hematology; Oncology; Phosphoprotein phosphatases; Protein kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Pan R, et al. Selective BCL-2 inhibition by ABT-199 causes on-target cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(3):362–375. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blombery P, et al. Acquisition of the recurrent Gly101Val mutation in BCL2 confers resistance to venetoclax in patients with progressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(3):342–353. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1119. - DOI - PubMed

