Pathways explaining racial/ethnic and socio-economic disparities in dementia incidence: the UK Biobank study
- PMID: 37751591
- PMCID: PMC10564412
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205058
Pathways explaining racial/ethnic and socio-economic disparities in dementia incidence: the UK Biobank study
Abstract
Background: Pathways explaining racial/ethnic disparities in dementia risk are under-evaluated.
Methods: We examine those disparities and their related pathways among UK Biobank study respondents (50-74 y, N = 323,483; 3.6% non-White minorities) using a series of Cox proportional hazards and generalized structural equations models (GSEM).
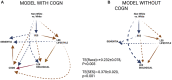
Results: After ≤15 years, 5,491 all-cause dementia cases were diagnosed. Racial minority status (RACE_ETHN, Non-White vs. White) increased dementia risk by 24% (HR = 1.24, 95% CI: 1.07-1.45, P = 0.005), an association attenuated by socio-economic status (SES), (HR = 1.12, 95% CI: 0.96-1.31). Total race-dementia effect was mediated through both SES and Life's Essential 8 lifestyle sub-score (LE8LIFESTYLE), combining diet, smoking, physical activity, and sleep factors. SES was inversely related to dementia risk (HR = 0.69, 95% CI: 0.67, 0.72, P < 0.001). Pathways explaining excess dementia risk among racial minorities included 'RACE_ETHN(-) → SES(-) → DEMENTIA', 'RACE_ETHN(-) → SES(-) → Poor cognitive performance, COGN(+) → DEMENTIA' and 'RACE_ETHN(-) → SES(+) → LE8LIFESTYLE(-) → DEMENTIA'.
Conclusions: Pending future interventions, lifestyle factors including diet, smoking, physical activity, and sleep are crucial for reducing racial and socio-economic disparities in dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dementia; health disparities; socio-economic status; structural equations modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, et al. , and Alzheimer’s Disease International. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2005; 366:2112–7. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

