Long-Term Safety Profiles of Macrolides and Tetracyclines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37751595
- PMCID: PMC11949418
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.2358
Long-Term Safety Profiles of Macrolides and Tetracyclines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
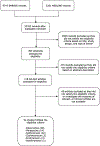
Macrolides and tetracyclines are antibiotics that have a range of anti-inflammatory properties beyond their microbial capabilities. Although these antibiotics have been in widespread use, the long-term safety profiles are limited. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials that compared macrolides or tetracyclines with placeboes to provide long-term safety information. We searched Medline and EMBASE from inception to October 2022 and identified studies that reported study drug-related death, serious adverse events (SAEs), or withdrawal rates, and common adverse effects of each drug. Relative risk (RR) and number needed to harm were calculated. Of the 52 randomized clinical trials included, there are 3151 participants on doxycycline, 2519 participants on minocycline, 3049 participants on azithromycin, 763 participants on clarithromycin, 262 participants on erythromycin, and 100 participants on roxithromycin. There was no death related to any study drugs and rates of SAE were not significantly different from placebo in any drug. Overall withdrawal rates were slightly higher than placebo in doxycycline (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.12-1.52) and minocycline (RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.15-1.46). Withdrawal rates due to adverse events were higher in doxycycline (RR, 2.82; 95% CI, 1.88-4.22), minocycline (RR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.09-1.98), and azithromycin (RR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.13-2.08). Gastrointestinal disturbances are the most common tolerable adverse effects for every drug. Photosensitivity and rash are the second most common adverse effects for doxycycline and minocycline. We found no evidence that long-term use up to 2 years of macrolides or tetracyclines was associated with increased risk of SAEs.
Keywords: adverse effects; adverse events; macrolides; safety; tetracyclines.
© 2023, The American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic antibiotics for adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 15;1(1):CD013198. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013198.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33448349 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Macrolide antibiotics for bronchiectasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 15;3(3):CD012406. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012406.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29543980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and safety of tetracyclines and quinolones in people with Mycoplasma pneumonia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Apr 4;71:102589. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102589. eCollection 2024 May. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38596615 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline in chronic management of febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): a case series and literature review of treatment strategies.Acta Epileptol. 2025 Jun 6;7(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s42494-025-00224-4. Acta Epileptol. 2025. PMID: 40481521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promises, Pitfalls, and Progress: Doxycycline Prophylaxis for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025 Feb 19;22(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s11904-025-00726-3. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025. PMID: 39969650 Review.
-
Correlation of lymphocyte-to-monocyte, platelet-to-lymphocyte, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios with skin-symptom improvement following antimicrobial treatment in palmoplantar pustulosis.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2025 Aug 14;11(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40780-025-00479-6. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2025. PMID: 40813703 Free PMC article.
-
What is the role of microbial biotechnology and genetic engineering in medicine?Microbiologyopen. 2024 Apr;13(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1406. Microbiologyopen. 2024. PMID: 38556942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kricker JA, Page CP, Gardarsson FR, Baldursson O, Gudjonsson T, Parnham MJ. Nonantimicrobial actions of macrolides: overview and perspectives for future development. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):233–262. - PubMed
-
- Castaldo RS, Celli BR, Gomez F, LaVallee N, Souhrada J, Hanrahan JP. A comparison of 5-day courses of dirithromycin and azithromycin in the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Ther. 2003;25(2):542–557. - PubMed
-
- Swanson RN, Lainez-Ventosilla A, De Salvo MC, Dunne MW, Amsden GW. Once-daily azithromycin for 3 days compared with clarithromycin for 10 days for acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized study. Treat Respir Med. 2005;4(1):31–39. - PubMed
-
- Akhyani M, Ehsani AH, Ghiasi M, Jafari AK. Comparison of efficacy of azithromycin vs. doxycycline in the treatment of rosacea: a randomized open clinical trial. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47(3):284–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources