Site-Selective Nitration of Aryl Germanes at Room Temperature
- PMID: 37751597
- PMCID: PMC11325643
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c02822
Site-Selective Nitration of Aryl Germanes at Room Temperature
Abstract
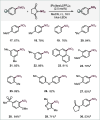
We report a site-selective ipso-nitration of aryl germanes in the presence of boronic esters, silanes, halogens, and additional functionalities. The protocol is characterized by operational simplicity, proceeds at room temperature, and is enabled by [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2/blue light photocatalysis. Owing to the exquisite robustness of the [Ge] functionality, nitrations of alternative functional handles in the presence of the germane are also feasible, as showcased herein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Orthogonal Olefination with Organogermanes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023 Oct 23;62(43):e202310380. doi: 10.1002/anie.202310380. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023. PMID: 37698171
-
Organogermanes as Orthogonal Coupling Partners in Synthesis and Catalysis.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Nov 17;53(11):2715-2725. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00527. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 33118804
-
Orthogonal Stability and Reactivity of Aryl Germanes Enables Rapid and Selective (Multi)Halogenations.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Oct 12;59(42):18717-18722. doi: 10.1002/anie.202008372. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32656881 Free PMC article.
-
Ipso-Nitration of Boronic Esters Enabled by Ferric Nitrate Nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O) in HFIP.Org Lett. 2025 Mar 28;27(12):2997-3002. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c00635. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Org Lett. 2025. PMID: 40079791
-
Orthogonal Nanoparticle Catalysis with Organogermanes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Dec 2;58(49):17788-17795. doi: 10.1002/anie.201910060. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31562670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Base-Catalyzed Remote Hydrogermylation of Olefins.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 May 26;64(22):e202503573. doi: 10.1002/anie.202503573. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40080055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faller J. W.; Kultyshev R. G. Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions of Allyl, Phenyl, Alkenyl, and Alkynyl Germatranes with Aryl Iodides. Organometallics 2002, 21, 5911–5918. 10.1021/om020578c. - DOI
- Nakamura T.; Kinoshita H.; Shinokubo H.; Oshima K. Biaryl Synthesis from Two Different Aryl Halides with Tri(2-furyl)germane. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3165–3167. 10.1021/ol026613t. - DOI - PubMed
- Spivey A. C.; Gripton C. J. G.; Hannah J. P.; Tseng C.-C.; de Fraine P.; Parr N. J.; Scicinski J. J. The development of a ‘safety-catch’ arylgermane for biaryl synthesis by palladium-catalysed germyl-stille cross-coupling. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 21, 572–589. 10.1002/aoc.1270. - DOI
-
- Fricke C.; Sherborne G. J.; Funes-Ardoiz I.; Senol E.; Guven S.; Schoenebeck F. Orthogonal Nanoparticle Catalysis with Organogermanes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17788–17795. 10.1002/anie.201910060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Fricke C.; Dahiya A.; Reid W. B.; Schoenebeck F. Gold-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization with Aryl Germanes. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9231–9236. 10.1021/acscatal.9b02841. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sherborne G. J.; Gevondian A. G.; Funes-Ardoiz I.; Dahiya A.; Fricke C.; Schoenebeck F. Modular and Selective Arylation of Aryl Germanes (C–GeEt3) over C–Bpin, C–SiR3 and Halogens Enabled by Light-Activated Gold Catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15543–15548. 10.1002/anie.202005066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dahiya A.; Schoenebeck F. Orthogonal and Modular Arylation of Alkynylgermanes. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 8048–8054. 10.1021/acscatal.2c02179. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

