Development and validation of a machine learning-based nomogram for predicting HLA-B27 expression
- PMID: 37752439
- PMCID: PMC10521518
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-023-00566-z
Development and validation of a machine learning-based nomogram for predicting HLA-B27 expression
Abstract
Background: HLA-B27 positivity is normal in patients undergoing rheumatic diseases. The diagnosis of many diseases requires an HLA-B27 examination.
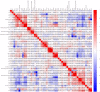
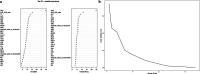
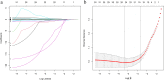
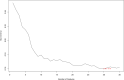
Methods: This study screened totally 1503 patients who underwent HLA-B27 examination, liver/kidney function tests, and complete blood routine examination in First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University. The training cohort included 509 cases with HLA-B27 positivity whereas 611 with HLA-B27 negativity. In addition, validation cohort included 147 cases with HLA-B27 positivity whereas 236 with HLA-B27 negativity. In this study, 3 ML approaches, namely, LASSO, support vector machine (SVM) recursive feature elimination and random forest, were adopted for screening feature variables. Subsequently, to acquire the prediction model, the intersection was selected. Finally, differences among 148 cases with HLA-B27 positivity and negativity suffering from ankylosing spondylitis (AS) were investigated.
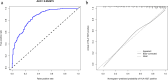
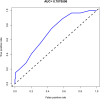
Results: Six factors, namely red blood cell count, human major compatibility complex, mean platelet volume, albumin/globulin ratio (ALB/GLB), prealbumin, and bicarbonate radical, were chosen with the aim of constructing the diagnostic nomogram using ML methods. For training queue, nomogram curve exhibited the value of area under the curve (AUC) of 0.8254496, and C-value of the model was 0.825. Moreover, nomogram C-value of the validation queue was 0.853, and the AUC value was 0.852675. Furthermore, a significant decrease in the ALB/GLB was noted among cases with HLA-B27 positivity and AS cases.
Conclusion: To conclude, the proposed ML model can effectively predict HLA-B27 and help doctors in the diagnosis of various immune diseases.
Keywords: HLA-B27; Immunological diseases; Machine learning algorithms; Nomogram; Prediction model.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Machine Learning-Based Nomogram for Prediction of Ankylosing Spondylitis.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Oct;9(5):1377-1397. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00481-6. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35932360 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a machine learning-based risk prediction model for cerebral infarction and comparison with nomogram model.J Affect Disord. 2022 Oct 1;314:341-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.07.045. Epub 2022 Jul 23. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35882300
-
Preoperative MRI-Based Radiomic Machine-Learning Nomogram May Accurately Distinguish Between Benign and Malignant Soft-Tissue Lesions: A Two-Center Study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Sep;52(3):873-882. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27111. Epub 2020 Feb 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32112598
-
The genetics of spondyloarthropathies.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2000 May;29(3):370-5. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2000. PMID: 10976392 Review.
-
[HLA-B27 in Bechterew's disease].Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2000 Apr 30;120(11):1317-22. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2000. PMID: 10868094 Review. Norwegian.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a diagnostic model to differentiate spinal tuberculosis from pyogenic spondylitis by combining multiple machine learning algorithms.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Mar 11;24(2):401-410. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9663. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 37897663 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring T Cell and NK Cell Involvement in Ankylosing Spondylitis Through Single-Cell Sequencing.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Dec;28(24):e70206. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70206. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39680481 Free PMC article.
-
The shared role of neutrophils in ankylosing spondylitis and ulcerative colitis.Genes Immun. 2024 Aug;25(4):324-335. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00286-3. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Genes Immun. 2024. PMID: 39060428
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

