Comparison of clinical outcomes and prognosis between surgery and endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with synchronous multifocal early gastric cancer
- PMID: 37752470
- PMCID: PMC10521562
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-023-02194-1
Comparison of clinical outcomes and prognosis between surgery and endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with synchronous multifocal early gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Synchronous multiple early gastric cancer (SMEGC) refers to the simultaneous occurrence of two or more malignant cancer lesions in the stomach. For patients with multiple early gastric carcinomas, the choice of appropriate treatment remains controversial. This study is dedicated to comparing the clinical outcomes and prognosis of patients with SMEGC who underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) or gastrectomy.
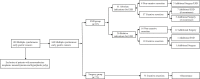
Methods: A total of 180 patients with more than one malignant cancer lesion in the stomach who had received gastrectomy or ESD between 2012 and 2021 were retrospectively evaluated to determine their clinical outcomes and prognosis. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were utilized to identify risk factors for tumor recurrence.
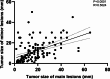
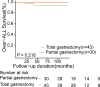
Results: Over the 57.5 months median follow-up period for the 140 enrolled cases, tumor recurrence occurred in 8 (12%) in the ESD group but only 1 (1%) in the surgery group. Relapse-free survival (RFS) was higher in the surgery group (p = 0.023) in all cases; however, there was no significant difference in Overall survival (OS, p = 0.772). Complications were significantly higher in the surgery group than in the ESD group, but fewer in the radical distal gastrectomy group. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that ESD(p = 0.034), the main lesion size > 2 cm(p = 0.019), and undifferentiated tumor(p = 0.022) were independent risk factors for tumor recurrence.
Conclusions: For the treatment of simultaneous multifocal early gastric cancer, ESD has a good short-term effect and higher quality of life. However, ESD has a higher risk of recurrence than surgery. And we found that the partial gastrectomy appears to be considered as adequate treatment for some SMEGC patients.
Keywords: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Prognosis; Surgical treatment; Synchronous multiple neoplasms.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the clinical and prognosis risk factors between endoscopic resection and radical gastrectomy for early-stage gastric cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 May 12;21(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03018-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37173790 Free PMC article.
-
[Efficacy comparison between surgical resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer in a domestic single center].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 25;21(2):190-195. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29492919 Chinese.
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgical resection for early gastric cancer: a retrospective multicenter study on immediate and long-term outcome over 5 years.Surg Endosc. 2016 Dec;30(12):5283-5289. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4877-y. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 27338583
-
Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgery in early gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr;31(4):418-424. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001352. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30694909
-
Updated evaluation of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgery for early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2020 Jan;73:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.11.027. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31783166
References
-
- Saragoni L, Morgagni P, Gardini A, Marfisi C, Vittimberga G, Garcea D, et al. Early gastric cancer: diagnosis, staging, and clinical impact. Evaluation of 530 patients. New elements for an updated definition and classification. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16(4):549–54. doi: 10.1007/s10120-013-0233-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

