The beneficial effects of simultaneous supplementation of Lactobacillus reuteri and calcium fluoride nanoparticles on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis
- PMID: 37752485
- PMCID: PMC10521537
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04167-6
The beneficial effects of simultaneous supplementation of Lactobacillus reuteri and calcium fluoride nanoparticles on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis
Abstract
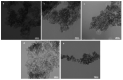
Background: The development of new strategies to inhibit and/or treat osteoporosis as a chronic systemic disease is one of the most crucial topics. The present study aimed to investigate the simultaneous effects of calcium fluoride nanoparticles (CaF2 NPs) and lactobacillus reuteri ATCC PTA 6475 (L. reuteri) against osteoporosis in an ovariectomized rat model (OVX).
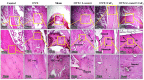
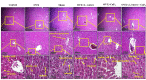
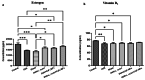
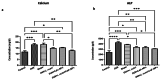
Methods: In this study, 18 matured Wistar female rats were randomly assigned into 6 groups, including control, OVX, sham, OVX + L. reuteri, OVX + CaF2 NPs, and OVX + L. reuteri + CaF2 NPs. We used OVX rats to simulate post-menopausal osteoporosis, and the treatments were begun two weeks before OVX and continued for four weeks. All groups' blood samples were collected, and serum biomarkers (estrogen, calcium, vitamin D3, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP)) were measured. The tibia and Femur lengths of all groups were measured. Histopathological slides of tibia, kidney, and liver tissues were analyzed using the Hematoxylin and Eosin staining method.
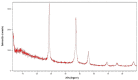
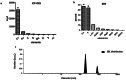
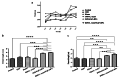
Results: Our results revealed that dietary supplementation of L. reuteri and CaF2 NPs in low doses for 6 weeks did not show adverse effects in kidney and liver tissues. The tibial and femoral lengths of OVX rats as well as the population of osteoblasts and osteocytes and newly generated osteoid in the tibia remarkably increased in the combination therapy group. Moreover, there was a significant increase in serum estrogen levels and a significant decrease in serum calcium and alkaline phosphatase levels in combination treatment groups compared to the OVX groups not receiving the diet.
Conclusions: Our results suggest the favorable effects of the simultaneous supplementation of L. reuteri and CaF2 NP to reduce post-menopausal bone loss.
Keywords: Bone biomarkers; Calcium fluoride nanoparticles; Lactobacillus reuteri; Osteoporosis; Ovariectomy.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Supportive Role of Probiotic Strains in Protecting Rats from Ovariectomy-Induced Cortical Bone Loss.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Dec;11(4):1145-1154. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9443-6. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 30014348
-
Olive oil effectively mitigates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Feb 4;11:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-10. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21294895 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-osteoporotic potential of a probiotic mixture containing Limosilactobacillus reuteri and Weissella cibaria in ovariectomized rats.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02089-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425630 Free PMC article.
-
Nigella Sativa reverses osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 14;14:22. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-22. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24422662 Free PMC article.
-
A traditional Chinese herbal preparation, Er-Zhi-Wan, prevent ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):279-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.030. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22001072 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress of research on the gut microbiome and its metabolite short-chain fatty acids in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a literature review.Front Med. 2025 Jun;19(3):474-492. doi: 10.1007/s11684-025-1129-3. Epub 2025 May 10. Front Med. 2025. PMID: 40347368 Review.
-
Anti-Menopausal Effect of Heat-Killed Bifidobacterium breve HDB7040 via Estrogen Receptor-Selective Modulation in MCF-7 Cells and Ovariectomized Rats.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 28;34(8):1580-1591. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2402.02035. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39081245 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota and Resveratrol: How Are They Linked to Osteoporosis?Cells. 2024 Jul 3;13(13):1145. doi: 10.3390/cells13131145. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TET1 mitigates prenatal fluoride-induced cognition impairment by modulating Bcl2 DNA hydroxymethylation level.Mol Med. 2025 Mar 25;31(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01174-w. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40133886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manolagas SC. Birth and death of bone cells: basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2000;21(2):115–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

