The Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation on Mood and Quality of Life in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37753046
- PMCID: PMC10519648
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44177
The Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation on Mood and Quality of Life in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
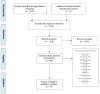
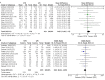
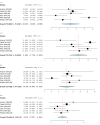
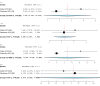
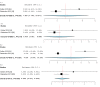
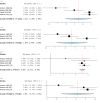
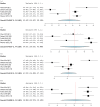
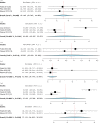
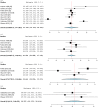
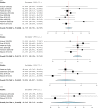
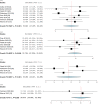
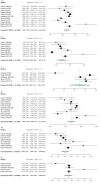
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is extensively used to treat motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease (PD). The aim of this study was to investigate the difference between subthalamic (STN) and globus pallidus internus (GPi) DBS on mood and quality of life with reference to minimal clinically important differences (MCID). A systematic literature search for articles published until November 2022 yielded 14 studies meeting the eligibility criteria, with a total of 1,088 patients undergoing STN (n=571) or GPi (n=517) stimulation. Baseline patient and clinical characteristics were comparable between the two groups. Results showed that GPi stimulation demonstrated a greater reduction in the Beck depression inventory (mean difference (MD)=1.68) than STN stimulation (MD=0.84). Hospital anxiety and depression scale showed a 2.69- and 3.48-point decrease by the GPi group in the depression and anxiety categories, respectively. The summary index (SI) of the PD questionnaire depicted a greater improvement in the GPi group from baseline (mean=41.01, 95% CI 34.89, 47.13) to follow-up (mean=30.85, 95% CI 22.08, 39.63) when compared to the STN group (baseline mean=42.43, 95% CI 34.50, 50.37; follow-up mean=34.21, 95% CI 25.43, 42.99). The emotions category also demonstrated a similar trend. However, STN stimulation showed greater reductions in motor symptoms and medication than GPi stimulation. This meta-analysis demonstrated that GPi stimulation seems to offer an advantage over STN stimulation in improving mood and quality of life in PD, but those effects must be further validated by larger studies.
Keywords: deep brain stimulation; globus pallidus internus; non-motor symptoms; parkinson's disease; subthalamic nucleus.
Copyright © 2023, El Ghazal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis comparing deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus to treat advanced Parkinson disease.J Neurosurg. 2014 Sep;121(3):709-18. doi: 10.3171/2014.4.JNS131711. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24905564
-
Efficacies of globus pallidus stimulation and subthalamic nucleus stimulation for advanced Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Interv Aging. 2016 Jun 21;11:777-86. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S105505. eCollection 2016. Clin Interv Aging. 2016. PMID: 27382262 Free PMC article.
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Patients With Parkinson's Disease: Executive Summary.Neurosurgery. 2018 Jun 1;82(6):753-756. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy037. Neurosurgery. 2018. PMID: 29538685 Free PMC article.
-
Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: meta-analysis of results of randomized trials at varying lengths of follow-up.J Neurosurg. 2018 Apr;128(4):1199-1213. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS16715. Epub 2017 Jun 30. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28665252
-
STN versus GPi deep brain stimulation for dyskinesia improvement in advanced Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Feb;201:106450. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106450. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33421741
Cited by
-
Alpha Synuclein Toxicity and Non-Motor Parkinson's.Cells. 2024 Jul 27;13(15):1265. doi: 10.3390/cells13151265. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case report: combined posterior subthalamic area and globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Jul 29;19:1638834. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1638834. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40799469 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the subthalamic nucleus.Commun Biol. 2024 Jan 10;7(1):78. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05691-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38200143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of Amyloid-β on the association between Orexin-A and blood-brain barrier leakage of globus pallidus in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with lewy bodies.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jun 2;17(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01770-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40457423 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
