Physicochemical and microbiological attributes of dried anchovies (Stolephorus commersonnii) in the formation of histamine along the supply chain
- PMID: 37753205
- PMCID: PMC10518830
- DOI: 10.4081/ijfs.2023.11319
Physicochemical and microbiological attributes of dried anchovies (Stolephorus commersonnii) in the formation of histamine along the supply chain
Abstract
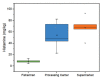
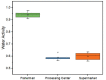
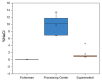
Food safety along the supply chain must be safeguarded to protect the public's health from any foodborne disease. Despite the consumption of fish products, scombroid poisoning is not a wellknown occurrence. This study was formulated to evaluate at which stage of the supply chain the increase in the histamine content of dried anchovies (Stolephorus commersonnii) occurs. The study showed that histamine substances and Staphylococcus aureus were detected at all stages of the supply chain. It was also found that the concentration of histamine generally increased from the fisherman to the processors and retailers. Post-hoc analysis using the Fisher test showed no significant difference in the histamine content of dried anchovies from the processing centers (𝑥̅ =5 4.07 mg/kg) and retailers (𝑥̅ = 67.63 mg/kg), but it was significantly higher than in the raw anchovies (𝑥̅ = 8.29 mg/kg). S. aureus remains low at <10 colony-forming units (CFU/g). The aerobic plate count supports this conclusion with a 90.29% increase from the processing centers to the retailers. However, it is still significant as a source of histamine formation influenced by water activity and salt content. A correlation between salt content and water activity with histamine content was identified with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.8357. It is recommended to review the processing method to control the salt content and the handling and storage at the retailers, as they showed the highest potential for histamine-forming bacteria growth, leading to an increase in histamine levels in dried anchovies.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus.; Stolephorus commersonnii; food safety; foodborne disease; histamine-forming bacteria.
Copyright © 2023, the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- D’sa EM, Harrison MA, 2005. Effect of pH, NaCl content, and temperature on growth and survival of Arcobacter spp. J Food 68:18-25. - PubMed
-
- Feldhusen F, 2000. The role of seafood in bacterial foodborne diseases. Microbes Infect 2:1651-60. - PubMed
-
- Fennema OR, 1996. Food chemistry (3rd ed). New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker.
-
- Ferran M, Yébenes M, 2006. Flushing associated with scombroid fish poisoning. Dermatol Online J 12:15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

