How does NFAT3 regulate the occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy?
- PMID: 37753338
- PMCID: PMC10518445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2023.101271
How does NFAT3 regulate the occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy?
Abstract
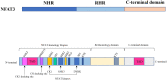
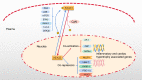
Cardiac hypertrophy is initially an adaptive response to physiological and pathological stimuli. Although pathological myocardial hypertrophy is the main cause of morbidity and mortality, our understanding of its mechanism is still weak. NFAT3 (nuclear factor of activated T-cell-3) is a member of the nuclear factor of the activated T cells (NFAT) family. NFAT3 plays a critical role in regulating the expression of cardiac hypertrophy genes by inducing their transcription. Recently, accumulating evidence has indicated that NFAT3 is a potent regulator of the progression of cardiac hypertrophy. This review, for the first time, summarizes the current studies on NFAT3 in cardiac hypertrophy, including the pathophysiological processes and the underlying pathological mechanism, focusing on the nuclear translocation and transcriptional function of NFAT3. This review will provide deep insight into the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy and a theoretical basis for identifying new therapeutic targets in the NFAT3 network.
Keywords: Cardiac hypertrophy; NFAT3; Nuclear translocation.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NULP1 Alleviates Cardiac Hypertrophy by Suppressing NFAT3 Transcriptional Activity.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Aug 18;9(16):e016419. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016419. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32805187 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of oxidants and AP-1 in angiotensin II-activated NFAT3 transcription factor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):C1248-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00624.2005. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17108007
-
The function of LncRNA-H19 in cardiac hypertrophy.Cell Biosci. 2021 Aug 3;11(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00668-4. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34344446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing roles of FoxP1 and Nfat3 in transcriptional control of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(14):3068-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00925-10. Epub 2011 May 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. Retraction in: Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Dec 21;41(1):e00544-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00544-20. PMID: 21606195 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The role and molecular mechanism of FoxO1 in mediating cardiac hypertrophy.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Dec;7(6):3497-3504. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13065. Epub 2020 Oct 22. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 33089967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Viola J.P., Carvalho L.D., Fonseca B.P., Teixeira L.K. NFAT transcription factors: from cell cycle to tumor development. Brazilian J. Med. Biol. Res. = Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas. 2005;38(3):335–344. - PubMed
-
- Hernández-Ochoa E.O., Robison P., Contreras M., Shen T., Zhao Z., Schneider M.F. Elevated extracellular glucose and uncontrolled type 1 diabetes enhance NFAT5 signaling and disrupt the transverse tubular network in mouse skeletal muscle. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2012;237(9):1068–1083. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

