The clinical relevance of acute-on-chronic liver failure in medical procedures: Endoscopy, interventions and surgery
- PMID: 37753553
- PMCID: PMC11815627
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.15749
The clinical relevance of acute-on-chronic liver failure in medical procedures: Endoscopy, interventions and surgery
Abstract
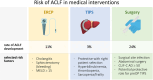
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a specific, but complex and multifactorial form of acute decompensation (AD) of cirrhosis and is characterized by an extraordinary dynamic natural course, rapidly evolving organ failure and high short-term mortality. In daily clinical practice, patients with liver cirrhosis and decompensation have indications for different medical procedures such as endoscopies, interventional treatments like transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) or even surgical procedures. In these situations, clinicians often need to balance the expected benefits of such procedures with the risks of causing acute decompensation or ACLF. This review summarizes the evidence of medical procedures and their role in precipitating or preventing ACLF and highlights the aspects to consider during patient selection.
Keywords: TIPS; acute‐on‐chronic liver failure; cirrhosis‐associated immune dysfunction; endoscopy; surgery.
© 2023 The Authors. Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Trebicka J, Schierwagen R. Hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: read‐out or reason? Hepatology. 2016;63(5):1729‐1732. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi M, Moreau R, Angeli P, Schnabl B, Arroyo V. Mechanisms of decompensation and organ failure in cirrhosis: from peripheral arterial vasodilation to systemic inflammation hypothesis. J Hepatol. 2015;63(5):1272‐1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical