MMP-2 Associates With Incident Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: The ARIC Study
- PMID: 37753653
- PMCID: PMC10842537
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.123.010849
MMP-2 Associates With Incident Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: The ARIC Study
Abstract
Background: MMP (matrix metalloproteinase)-2 participates in extracellular matrix regulation and may be involved in heart failure (HF), atrial fibrillation (AF), and coronary heart disease.
Methods: Among the 4693 ARIC study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) participants (mean age, 75±5 years; 42% women) without prevalent HF, multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate associations of plasma MMP-2 levels with incident HF, HF with preserved ejection fraction (≥50%), HF with reduced ejection fraction (<50%), AF, and coronary heart disease. Mediation of the association between MMP-2 and HF was assessed by censoring participants who developed AF or coronary heart disease before HF. Multivariable linear regression models were used to assess associations of MMP-2 with measures of left ventricular and left atrial structure and function.
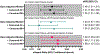
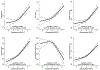
Results: Compared with the 3 lower quartiles, the highest MMP-2 quartile associated with greater risk of incident HF overall (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.48 [95% CI, 1.21-1.81]), incident HF with preserved ejection fraction (1.44 [95% CI, 1.07-1.94]), incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (1.48 [95% CI, 1.08-2.02]), and incident AF (1.44 [95% CI, 1.18-1.77]) but not incident coronary heart disease (0.97 [95% CI, 0.71-1.34]). Censoring AF attenuated the MMP-2 association with HF with preserved ejection fraction. Higher plasma MMP-2 levels were associated with larger left ventricular end-diastolic volume index, greater left ventricular mass index, higher E/e' ratio, larger left atrial volume index, and worse left atrial reservoir and contractile strains (all P<0.001).
Conclusions: Higher plasma MMP-2 levels associate with diastolic dysfunction, left atrial dysfunction, and a higher risk of incident HF and AF. AF is a mediator of MMP-2-associated HF with preserved ejection fraction risk.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; echocardiography; epidemiology; heart failure; matrix metalloproteinases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
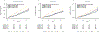
Similar articles
-
Atrial Fibrillation Begets Heart Failure and Vice Versa: Temporal Associations and Differences in Preserved Versus Reduced Ejection Fraction.Circulation. 2016 Feb 2;133(5):484-92. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018614. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 26746177 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Features of Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Dec 10;74(23):2858-2873. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.063. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31806129 Clinical Trial.
-
Atrial fibrillation and risk of incident heart failure with reduced versus preserved ejection fraction.Heart. 2022 Mar;108(5):353-359. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2021-319122. Epub 2021 May 24. Heart. 2022. PMID: 34031160 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Atrial Fibrillation Across the Spectrum of Heart Failure With Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction.Circulation. 2022 Jul 26;146(4):339-357. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.057444. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35877831 Review.
-
Does Left Ventricular Systolic Function Matter? Treating Atrial Fibrillation in HFrEF Versus HFpEF.Cardiol Clin. 2019 May;37(2):157-166. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2019.01.008. Cardiol Clin. 2019. PMID: 30926017 Review.
Cited by
-
Senescence Biomarkers and Trajectories of Frailty and Physical Function After Kidney Transplantation.Clin Transplant. 2024 Nov;38(11):e70022. doi: 10.1111/ctr.70022. Clin Transplant. 2024. PMID: 39564682
-
Factors predicting the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: A review.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 6;10(13):e34205. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34205. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening for Heart Failure: Biomarkers to Detect Heightened Risk in the General Population.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2024 Dec;21(6):591-603. doi: 10.1007/s11897-024-00686-6. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2024. PMID: 39287754 Review.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases: Pathophysiologic Implications and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 17;15(4):598. doi: 10.3390/biom15040598. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure Impairs Fetal Heart Development: Molecular and Structural Alterations with Sex-Specific Differences.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 14;14(7):863. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070863. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roger Veronique L. Epidemiology of Heart Failure: A Contemporary Perspective. Circ Res. 2021;128:1421–1434. - PubMed
-
- Triposkiadis F, Xanthopoulos A, Butler J. Cardiovascular Aging and Heart Failure: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:804–813. - PubMed
-
- López B, Ravassa S, Moreno MU, José GS, Beaumont J, González A, Díez J. Diffuse myocardial fibrosis: mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:479–498. - PubMed
-
- Nagibin V, Egan Benova T, Viczenczova C, Szeiffova Bacova B, Dovinova I, Barancik M, Tribulova N. Ageing related down-regulation of myocardial connexin-43 and up-regulation of MMP-2 may predict propensity to atrial fibrillation in experimental animals. Physiol Res. 2016;65 Suppl 1:S91–s100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 HL150311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135008/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL150342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148218/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL143224/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL152008/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL160025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

