Recent advances in exosomal non-coding RNA-based therapeutic approaches for photoaging
- PMID: 37753673
- PMCID: PMC10495620
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13463
Recent advances in exosomal non-coding RNA-based therapeutic approaches for photoaging
Abstract
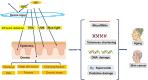
Background: Photoaging is a degenerative biological process that affects the quality of life. It is caused by environmental factors including ultraviolet radiation (UVR), deep skin burns, smoking, active oxygen, chemical substances, and trauma. Among them, UVR plays a vital role in the aging process.
Aim: With the continuous development of modern medicine, clinical researchers have investigated novel approaches to treat aging. In particular, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), non-coding RNAs are involved in various physiological processes have broad clinical application as they have the advantages of convenient samples, abundant sources, and avoidable ethical issues.
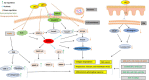
Methods: This article reviews research progress on five types of stem cell, exosomes, non-coding RNA in the context of photoaging treatment: adipose-derived stem cell, human umbilical cord MSCs, epidermal progenitor cells, keratinocyte stem cells, and hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs). It also includes stem cell related exosomes and their non-coding RNA research.
Results: The results have clinical guiding significance for prevention and control of the onset and development of photoaging. It is found that stem cells secrete cytokines, cell growth factors, non-coding RNA, exosomes and proteins to repair aging skin tissues and achieve skin rejuvenation. In particular, stem cell exosomes and non-coding RNA are found to have significant research potential, as they possess the benefits of their source cells without the disadvantages which include immune rejection and granuloma formation.
Keywords: exosome; mesenchymal stem cells; non-coding RNA; photoaging; skin cancer; ultraviolet radiation.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Todorova K, Mandinova A. Novel approaches for managing aged skin and nonmelanoma skin cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;153:18‐27. - PubMed
-
- Krutmann J, Berneburg M. [Sun‐damaged skin (photoaging): what is new?]. Hautarzt . 2021;72(1):2‐5. - PubMed
-
- Beylot C. [Skin ageing‐General features of facial ageing and therapeutic choices]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2019;146(1):41‐74. - PubMed
-
- Dai N‐T, Chang H‐I, Wang Y‐W, et al. Restoration of skin pigmentation after deep partial or full‐thickness burn injury. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;123:155‐164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

