Topical dexpanthenol effects on physiological parameters of the stratum corneum by Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy
- PMID: 37753694
- PMCID: PMC10504581
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13317
Topical dexpanthenol effects on physiological parameters of the stratum corneum by Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy
Abstract
Background: Topical use of dexpanthenol presents well-established moisturizing properties and maintenance and repair of the skin barrier function, however, its exact action mechanisms are not completely elucidated. In this context, Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy is an optical method that enables non-invasive and non-destructive in vivo analysis with the sensitive acquisition of molecular changes in different skin layers. Herein, the aim was to evaluate the effects of topical dexpanthenol on the components and physiological parameters of the stratum corneum (SC).
Materials and methods: Ten healthy female subjects underwent skin evaluation by means of a Confocal Raman Spectrometer Skin Analyzer 3510. Spectral data were obtained from the skin of the anterior forearm region, before and 2 h after applying a cosmetic formulation containing or not containing 5% dexpanthenol.
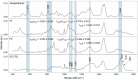
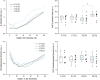
Results: Semiquantitative analysis of the natural moisturizing factor showed a significant decrease in content after 2 h of topical dexpanthenol application, while the analysis of the lamellar organization of intercellular lipids and the secondary structure of keratin showed a significant increase in hexagonal organization of lipids at the first half of the SC and a significant increase in β-pleated sheet conformation of keratin.
Conclusion: Effects of topical dexpanthenol on SC suggest a contribution in increasing fluidity of both lipidic and protein components of the SC and are compatible with dexpanthenol activity in maintaining adequate physiological conditions and preventing transepidermal water loss. This study also contributes to the elucidation of action mechanisms and other concurrent biochemical processes.
Keywords: dexpanthenol; intercellular lipids; natural moisturizing factor; skin barrier function.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Gustavo Carlos Silva is a PhD student at Dermo PROBES—Skin and Hair Technology and received a scholarship for this study. Airton Abrahão Martin is CEO of Dermo PROBES—Skin and Hair Technology. The authors acknowledge no other actual or potential conflict of interest with individuals or entities.
Figures




References
-
- Heise R, Skazik C, Marquardt Y, et al. Dexpanthenol modulates gene expression in skin wound healing in vivo. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Zoe D, Draelos MD. The science behind skin care: Moisturizers. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018;17:138–44. - PubMed
-
- Proksch E, Bony R, Trapp S, Boudon S. Topical use of dexpanthenol: A 70th anniversary article, J Dermatol Treat. 2017;28(8):766‐773. - PubMed
-
- Giménez‐Arnau A. Standards for the protection of skin barrier function. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2016;49:123–34. - PubMed
-
- Crowther JM. Understanding humectant behaviour through their water‐holding properties. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2021;43:601–609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

