Beliefs about the Nature of Forgiveness and Avoidance of an Offender among Chinese College Students
- PMID: 37754025
- PMCID: PMC10525877
- DOI: 10.3390/bs13090747
Beliefs about the Nature of Forgiveness and Avoidance of an Offender among Chinese College Students
Abstract
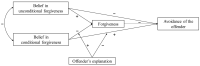
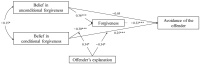
Previous research on beliefs about the nature of forgiveness (unconditional and conditional) has focused on their effects on health and well-being. However, little is known about how they influence victims' responses to interpersonal offenses. Given that avoidance is a common response to offenses during early adulthood, this study investigated the relationships between beliefs in unconditional and conditional forgiveness and avoidance of an offender among Chinese college students, the mediating role of forgiveness, and the moderating role of whether or not the offender explains the offense. Participants were 423 Chinese college students. They were asked to recall an unforgettable incident in which another person had offended them, and then completed the following measures: the offender's explanation, the belief in unconditional/conditional forgiveness, forgiveness, and avoidance of the offender. The study found that: (1) Victims' belief in unconditional forgiveness negatively predicts their avoidance of an offender, whereas their belief in conditional forgiveness positively predicts the avoidance of an offender. (2) Forgiveness mediates the relationships between beliefs in unconditional and conditional forgiveness and avoidance of an offender. (3) The offender's explanation moderates the relationships between the belief in conditional forgiveness and forgiveness, as well as avoidance of an offender.
Keywords: behavioral avoidance; belief about the nature of forgiveness; conditional forgiveness; explanation; forgiveness; interpersonal offense; unconditional forgiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Victim and offender accounts of interpersonal conflict: autobiographical narratives of forgiveness and unforgiveness.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2002 Apr;82(4):675-86. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2002. PMID: 11999931
-
Sincerity Is in the Eye of the Beholder: Using Eye Tracking to Understand How Victims Interpret an Offender's Apology in a Simulation of Victim-Offender Mediation.Front Psychol. 2020 May 20;11:835. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00835. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32508705 Free PMC article.
-
Love Forgiveness and Subjective Well-Being in Chinese College Students: The Mediating Role of Interpersonal Relationships.Front Psychol. 2021 Jun 4;12:634910. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.634910. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34149520 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionary psychology view of forgiveness: individuals, groups, and culture.Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Apr;44:275-280. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.021. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 34801844 Review.
-
Designing forgiveness interventions: guidance from five meta-analyses.J Holist Nurs. 2015 Jun;33(2):161-7. doi: 10.1177/0898010114560571. Epub 2014 Dec 8. J Holist Nurs. 2015. PMID: 25487180 Review.
References
-
- Bono G., McCullough M.E. Positive Responses to Benefit and Harm: Bringing Forgiveness and Gratitude into Cognitive Psychotherapy. J. Cogn. Psychother. 2006;20:147–158. doi: 10.1891/jcop.20.2.147. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources