Cost-Effective Modular Biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A Detection
- PMID: 37754108
- PMCID: PMC10526333
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13090874
Cost-Effective Modular Biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A Detection
Abstract
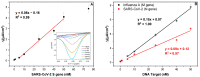
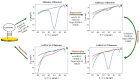
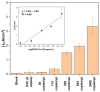
A modular, multi-purpose, and cost-effective electrochemical biosensor based on a five-stranded four-way junction (5S-4WJ) system was developed for SARS-CoV-2 (genes S and N) and Influenza A virus (gene M) detection. The 5S-4WJ structure consists of an electrode-immobilized universal stem-loop (USL) strand, two auxiliary DNA strands, and a universal methylene blue redox strand (UMeB). This design allows for the detection of specific nucleic acid sequences using square wave voltammetry (SWV). The sequence-specific auxiliary DNA strands (m and f) ensure selectivity of the biosensor for target recognition utilizing the same USL and UMeB components. An important feature of this biosensor is the ability to reuse the USL-modified electrodes to detect the same or alternative targets in new samples. This is accomplished by a simple procedure involving rinsing the electrodes with water to disrupt the 5S-4WJ structure and subsequent re-hybridization of the USL strand with the appropriate set of strands for a new analysis. The biosensor exhibited minimal loss in signal after rehybridization, demonstrating its potential as a viable multiplex assay for both current and future pathogens, with a low limit of quantification (LOQ) of as low as 17 pM.
Keywords: Influenza A; SARS-CoV-2; biosensor; four-way junction; microliter detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Single Electrochemical Probe Used for Analysis of Multiple Nucleic Acid Sequences.Electroanalysis. 2017 Mar;29(3):873-879. doi: 10.1002/elan.201600548. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Electroanalysis. 2017. PMID: 29371782 Free PMC article.
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, multiplexed, and nucleic acid amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using an electrochemical biosensor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Jan 1;195:113649. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113649. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 34555637 Free PMC article.
-
A label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor used a printed circuit board gold electrode (PCBGE) to detect SARS-CoV-2 without amplification.Lab Chip. 2023 Mar 14;23(6):1622-1636. doi: 10.1039/d2lc01159j. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 36786757
-
Fabrication of Electrochemical Influenza Virus (H1N1) Biosensor Composed of Multifunctional DNA Four-Way Junction and Molybdenum Disulfide Hybrid Material.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jan 12;14(2):343. doi: 10.3390/ma14020343. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33445498 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Single Electrochemical Biosensor Designed to Detect Any Virus.Anal Chem. 2024 Apr 16;96(15):5752-5756. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05962. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38560822 Free PMC article.
-
Highly reproducible electrochemical biosensor for Influenza A virus towards low-resource settings.Anal Methods. 2024 Feb 1;16(5):772-779. doi: 10.1039/d3ay01825c. Anal Methods. 2024. PMID: 38230437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kola L., Kohrt B.A., Hanlon C., Naslund J.A., Sikander S., Balaji M., Benjet C., Cheung E.Y.L., Eaton J., Gonsalves P., et al. COVID-19 mental health impact and responses in low-income and middle-income countries: Reimagining global mental health. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8:535–550. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00025-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hogan A.B., Jewell B.L., Sherrard-Smith E., Vesga J.F., Watson O.J., Whittaker C., Hamlet A., Smith J.A., Winskill P., Verity R., et al. Potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria in low-income and middle-income countries: A modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2020;8:e1132–e1141. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30288-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

