Circulating Tumor Cells Adhesion: Application in Biosensors
- PMID: 37754116
- PMCID: PMC10526177
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13090882
Circulating Tumor Cells Adhesion: Application in Biosensors
Abstract
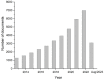
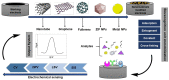
The early and non-invasive diagnosis of tumor diseases has been widely investigated by the scientific community focusing on the development of sensors/biomarkers that act as a way of recognizing the adhesion of circulating tumor cells (CTCs). As a challenge in this area, strategies for CTCs capture and enrichment currently require improvements in the sensors/biomarker's selectivity. This can be achieved by understanding the biological recognition factors for different cancer cell lines and also by understanding the interaction between surface parameters and the affinity between macromolecules and the cell surface. To overcome some of these concerns, electrochemical sensors have been used as precise, fast-response, and low-cost transduction platforms for application in cytosensors. Additionally, distinct materials, geometries, and technologies have been investigated to improve the sensitivity and specificity properties of the support electrode that will transform biochemical events into electrical signals. This review identifies novel approaches regarding the application of different specific biomarkers (CD44, Integrins, and EpCAm) for capturing CTCs. These biomarkers can be applied in electrochemical biosensors as a cytodetection strategy for diagnosis of cancerous diseases.
Keywords: CD44; EpCAm; circulating tumor cells; electrochemical biosensor; integrins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer. [(accessed on 1 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/
-
- Potdar P., Lotey N. Role of Circulating Tumor Cells in Future Diagnosis and Therapy of Cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2015;1:44. doi: 10.4103/2394-4722.158803. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

