Novel Cytochrome P450-3A4 Enzymatic Nanobiosensor for Lapatinib (a Breast Cancer Drug) Developed on a Poly(anilino-co-4-aminobenzoic Acid-Green-Synthesised Indium Nanoparticle) Platform
- PMID: 37754131
- PMCID: PMC10527071
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13090897
Novel Cytochrome P450-3A4 Enzymatic Nanobiosensor for Lapatinib (a Breast Cancer Drug) Developed on a Poly(anilino-co-4-aminobenzoic Acid-Green-Synthesised Indium Nanoparticle) Platform
Abstract
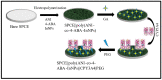
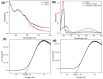
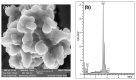
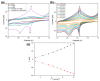
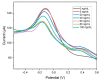
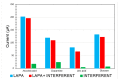
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most common types of cancer disease worldwide and it accounts for thousands of deaths annually. Lapatinib is among the preferred drugs for the treatment of breast cancer. Possible drug toxicity effects of lapatinib can be controlled by real-time determination of the appropriate dose for a patient at the point of care. In this study, a novel highly sensitive polymeric nanobiosensor for lapatinib is presented. A composite of poly(anilino-co-4-aminobenzoic acid) co-polymer {poly(ANI-co-4-ABA)} and coffee extract-based green-synthesized indium nanoparticles (InNPs) was used to develop the sensor platform on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE), i.e., SPCE||poly(ANI-co-4-ABA-InNPs). Cytochrome P450-3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme and polyethylene glycol (PEG) were incorporated on the modified platform to produce the SPCE||poly(ANI-co-4-ABA-InNPs)|CYP3A4|PEG lapatinib nanobiosensor. Experiments for the determination of the electrochemical response characteristics of the nanobiosensor were performed with cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The nanobiosensor calibration for 0-100 ng/mL lapatinib was linear and gave limit of detection (LOD) values of 13.21 ng/mL lapatinib and 18.6 ng/mL lapatinib in physiological buffer and human serum, respectively. The LOD values are much lower than the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of lapatinib (2.43 µg/mL), which is attained 4 h after the administration of a daily dose of 1250 mg lapatinib. The electrochemical nanobiosensor also exhibited excellent anti-interference performance and stability.
Keywords: biosensor; breast cancer drug (lapatinib); cytochrome P450-3A4; green-synthesized indium nanoparticles; polyaniline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced, or appeared to have influenced, the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon Fr. Int. Agency Res. Cancer. 2018;3:2019.
-
- Dos Santos A.F., De Almeida D.R.Q., Terra L.F., Baptista M.S., Labriola L. Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Treatment—An Update Review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019;5:1–32. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2018.83. - DOI
-
- Bhadra P., Deb A. Targeted Therapy for Cancer in Women Nutraceuticals View Project Role of Phytochemicals in Human Physiological Disorders: Diabetes and Obesity View Project. Indian J. Nat. Sci. 2020;10:20609–20616.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

