Adaptive Guided Equilibrium Optimizer with Spiral Search Mechanism to Solve Global Optimization Problems
- PMID: 37754134
- PMCID: PMC10526928
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics8050383
Adaptive Guided Equilibrium Optimizer with Spiral Search Mechanism to Solve Global Optimization Problems
Abstract
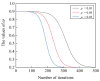
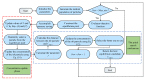
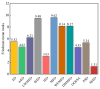
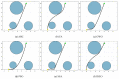
The equilibrium optimizer (EO) is a recently developed physics-based optimization technique for complex optimization problems. Although the algorithm shows excellent exploitation capability, it still has some drawbacks, such as the tendency to fall into local optima and poor population diversity. To address these shortcomings, an enhanced EO algorithm is proposed in this paper. First, a spiral search mechanism is introduced to guide the particles to more promising search regions. Then, a new inertia weight factor is employed to mitigate the oscillation phenomena of particles. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, it has been tested on the CEC2017 test suite and the mobile robot path planning (MRPP) problem and compared with some advanced metaheuristic techniques. The experimental results demonstrate that our improved EO algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in solving both numerical optimization problems and practical problems. Overall, the developed EO variant has good robustness and stability and can be considered as a promising optimization tool.
Keywords: equilibrium optimizer; global optimization; metaheuristics; mobile robot path planning; nature-inspired.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


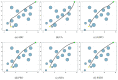
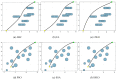
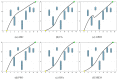
Similar articles
-
A chaos-based adaptive equilibrium optimizer algorithm for solving global optimization problems.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Sep 4;20(9):17242-17271. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023768. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37920054
-
Multi‑strategy Equilibrium Optimizer: An improved meta-heuristic tested on numerical optimization and engineering problems.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 20;17(10):e0276210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276210. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36264991 Free PMC article.
-
An enhanced snow ablation optimizer for UAV swarm path planning and engineering design problems.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 11;10(18):e37819. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37819. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39315149 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in use of bio-inspired jellyfish search algorithm for solving optimization problems.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 10;12(1):19157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23121-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36357444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the gazelle Optimizer and its variants.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 16;10(17):e36425. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36425. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the Efficiency of a Cybersecurity Operations Center Using Biomimetic Algorithms Empowered by Deep Q-Learning.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 May 21;9(6):307. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9060307. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gharehchopogh F.S. Quantum-inspired metaheuristic algorithms: Comprehensive survey and classification. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022;56:5479–5543. doi: 10.1007/s10462-022-10280-8. - DOI
-
- Wang Z., Ding H., Yang J., Wang J., Li B., Yang Z., Hou P. Advanced orthogonal opposition-based learning-driven dynamic salp swarm algorithm: Framework and case studies. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2022;16:945–971. doi: 10.1049/cth2.12277. - DOI
-
- Kaveh A., Zaerreza A. A new framework for reliability-based design optimization using metaheuristic algorithms. Structures. 2022;38:1210–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.02.069. - DOI
-
- Abdel-Basset M., Mohamed R., Azeem S.A.A., Jameel M., Abouhawwash M. Kepler optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic algorithm inspired by Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023;268:110454. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110454. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 61461054/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 61461053/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 61072079/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2022Y008/Yunnan Provincial Education Department Scientific Research Fund Project
- KC-22222706/the Yunnan University's Research Innovation Fund for Graduate Students
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

