A Navigation Path Search and Optimization Method for Mobile Robots Based on the Rat Brain's Cognitive Mechanism
- PMID: 37754178
- PMCID: PMC10526878
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics8050427
A Navigation Path Search and Optimization Method for Mobile Robots Based on the Rat Brain's Cognitive Mechanism
Abstract
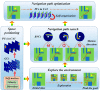
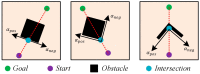
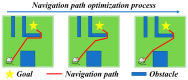
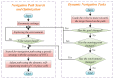
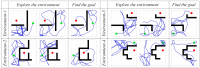
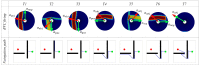
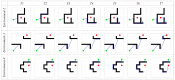
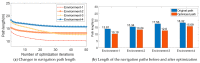
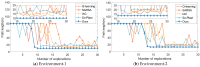
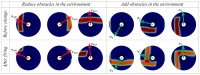
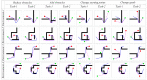
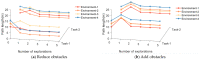
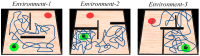
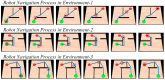
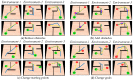
Rats possess exceptional navigational abilities, allowing them to adaptively adjust their navigation paths based on the environmental structure. This remarkable ability is attributed to the interactions and regulatory mechanisms among various spatial cells within the rat's brain. Based on these, this paper proposes a navigation path search and optimization method for mobile robots based on the rat brain's cognitive mechanism. The aim is to enhance the navigation efficiency of mobile robots. The mechanism of this method is based on developing a navigation habit. Firstly, the robot explores the environment to search for the navigation goal. Then, with the assistance of boundary vector cells, the greedy strategy is used to guide the robot in generating a locally optimal path. Once the navigation path is generated, a dynamic self-organizing model based on the hippocampal CA1 place cells is constructed to further optimize the navigation path. To validate the effectiveness of the method, this paper designs several 2D simulation experiments and 3D robot simulation experiments, and compares the proposed method with various algorithms. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method not only surpasses other algorithms in terms of path planning efficiency but also yields the shortest navigation path. Moreover, the method exhibits good adaptability to dynamic navigation tasks.
Keywords: boundary vector cells; mobile robots; navigation path; optimization; place cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Li Z.C., Jing X.J., Sun B., Yu J.Y. Autonomous navigation of a tracked mobile robot with novel passive bio-inspired suspension. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020;25:2633–2644. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2020.2987004. - DOI
-
- Zhu D., Yang S.X. Bio-inspired neural network-based optimal path planning for UUVs under the effect of ocean currents. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2021;7:231–239. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2021.3082151. - DOI
-
- Yuan J.S., Guo W., Hou Z.Y., Zha F.S., Li M.T., Sun L.I., Wang P.F. Robot Navigation Strategy in Complex Environment Based on Episode Cognition. J. Bionic Eng. 2023;20:1–15. doi: 10.1007/s42235-022-00265-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

