Recent Development and Application of "Nanozyme" Artificial Enzymes-A Review
- PMID: 37754197
- PMCID: PMC10526256
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics8050446
Recent Development and Application of "Nanozyme" Artificial Enzymes-A Review
Abstract
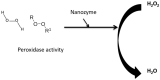
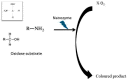
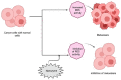
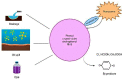
Nanozymes represent a category of nano-biomaterial artificial enzymes distinguished by their remarkable catalytic potency, stability, cost-effectiveness, biocompatibility, and degradability. These attributes position them as premier biomaterials with extensive applicability across medical, industrial, technological, and biological domains. Following the discovery of ferromagnetic nanoparticles with peroxidase-mimicking capabilities, extensive research endeavors have been dedicated to advancing nanozyme utilization. Their capacity to emulate the functions of natural enzymes has captivated researchers, prompting in-depth investigations into their attributes and potential applications. This exploration has yielded insights and innovations in various areas, including detection mechanisms, biosensing techniques, and device development. Nanozymes exhibit diverse compositions, sizes, and forms, resembling molecular entities such as proteins and tissue-based glucose. Their rapid impact on the body necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their intricate interplay. As each day witnesses the emergence of novel methodologies and technologies, the integration of nanozymes continues to surge, promising enhanced comprehension in the times ahead. This review centers on the expansive deployment and advancement of nanozyme materials, encompassing biomedical, biotechnological, and environmental contexts.
Keywords: biomimetic; catalytic; enzymatic; nanomaterial; nanozymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanozymes: From New Concepts, Mechanisms, and Standards to Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Aug 20;52(8):2190-2200. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00140. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31276379
-
Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, Activity Regulation, and Applications.Chem Rev. 2019 Mar 27;119(6):4357-4412. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00672. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30801188 Review.
-
In vivo guiding inorganic nanozymes for biosensing and therapeutic potential in cancer, inflammation and microbial infections.Talanta. 2021 Mar 1;224:121805. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121805. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 33379031 Review.
-
Recent Advancements in the Formulation of Nanomaterials-Based Nanozymes, Their Catalytic Activity, and Biomedical Applications.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Sep 18;6(9):3577-3599. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00253. Epub 2023 Aug 17. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37590090 Review.
-
Applications of Nanozymology in the Detection and Identification of Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 22;23(9):4638. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094638. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Nanozyme-Based Sensing Technology for Antioxidant Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 14;24(20):6616. doi: 10.3390/s24206616. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanozymes for Accelerating the Foot Wound Healing: A Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 10;20:8907-8934. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S517671. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40661658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: targeted nanozyme therapies and their clinical potential and current challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 28;23(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03590-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40717066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscience in Action: Unveiling Emerging Trends in Materials and Applications.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 17;10(8):7530-7548. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10929. eCollection 2025 Mar 4. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40060806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Flower-like MnMoO4 Nanostructures and Their Photocatalytic Performance.Materials (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;17(7):1451. doi: 10.3390/ma17071451. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen R., Hunt J.A. Biomimetic Materials Processing for Tissue-Engineering Processes. J. Mater. Chem. 2007;17:3974. doi: 10.1039/b706765h. - DOI
-
- Mukhopadhayay M., Chatterjee A. Classification of Foods, Biomaterials, and Microorganisms. In: Mukhopadhayay M., Chatterjee A., editors. Sterilization and Preservation: Applications of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2023. pp. 9–42.
-
- Liu S., Yu J.-M., Gan Y.-C., Qiu X.-Z., Gao Z.-C., Wang H., Chen S.-X., Xiong Y., Liu G.-H., Lin S.-E., et al. Biomimetic Natural Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: New Biosynthesis Methods, Recent Advances, and Emerging Applications. Mil. Med. Res. 2023;10:16. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00448-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

