Ouabain Induces Transcript Changes and Activation of RhoA/ROCK Signaling in Cultured Epithelial Cells (MDCK)
- PMID: 37754259
- PMCID: PMC10528288
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45090475
Ouabain Induces Transcript Changes and Activation of RhoA/ROCK Signaling in Cultured Epithelial Cells (MDCK)
Abstract
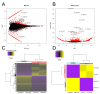
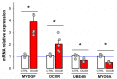
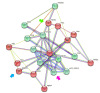
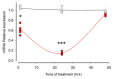
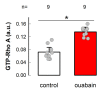
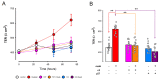
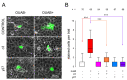
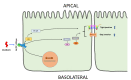
Ouabain, an organic compound with the ability to strengthen the contraction of the heart muscle, was originally derived from plants. It has been observed that certain mammalian species, including humans, naturally produce ouabain, leading to its classification as a new type of hormone. When ouabain binds to Na+/K+-ATPase, it elicits various physiological effects, although these effects are not well characterized. Previous studies have demonstrated that ouabain, within the concentration range found naturally in the body (10 nmol/L), affects the polarity of epithelial cells and their intercellular contacts, such as tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctional communication. This is achieved by activating signaling pathways involving cSrc and Erk1/2. To further investigate the effects of ouabain within the hormonally relevant concentration range (10 nmol/L), mRNA-seq, a high-throughput sequencing technique, was employed to identify differentially expressed transcripts. The discovery that the transcript encoding MYO9A was among the genes affected prompted an exploration of whether RhoA and its downstream effector ROCK were involved in the signaling pathways through which ouabain influences cell-to-cell contacts in epithelial cells. Supporting this hypothesis, this study reveals the following: (1) Ouabain increases the activation of RhoA. (2) Treatment with inhibitors of RhoA activation (Y27) and ROCK (C3) eliminates the enhancing effect of ouabain on the tight junction seal and intercellular communication via gap junctions. These findings further support the notion that ouabain acts as a hormone to emphasize the epithelial phenotype.
Keywords: MDCK; MYO9A; Na+/K+-ATPase; cell–cell contacts; epithelia; gene expression; ouabain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 439501, Ouabain. [(accessed on 9 May 2023)]; Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ouabain.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

