Diet, Nutrition, and Oral Health in Older Adults: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 37754342
- PMCID: PMC10528506
- DOI: 10.3390/dj11090222
Diet, Nutrition, and Oral Health in Older Adults: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
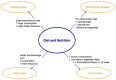
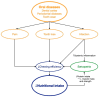
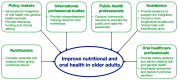
Diet, nutrition, and oral health are closely linked. Malnutrition is a challenging health concern in older adults that is associated with physical decline affecting their daily activities and quality of life. The aim of this review is to provide an evidence-based summary of the relationship between diet and nutrition and oral health in older adults and its implications. The World Health Organization has declared healthy ageing a priority of its work on ageing. The American Dental Association confirmed the bidirectional relationship between diet and nutrition and oral health. The literature shows that diet and nutrition are related to oral diseases, including dental caries, periodontal diseases, tooth wear, and even oral cancer. Insufficient nutritional intake and poor dietary habits increase the risk of oral diseases, such as dental caries, in older adults. On the other hand, in older adults, poor oral conditions such as periodontal disease may induce pain, infection, and tooth loss, affecting nutritional intake. Surveys have shown that older adults, in particular, those in disadvantaged communities, suffered from nutritional deficiencies or imbalances affecting their oral health. In addition, the current literature shows that malnutrition is associated with frailty, hospitalization, mortality, and morbidity. Good oral health and functional dentition are essential to maintain sufficient nutritional intake among older adults and reduce the risk of malnutrition. Therefore, integrating oral health into general health care service in older adults is imperative to improve their nutritional and oral health status to achieve healthy ageing.
Keywords: caries; diet; elderly; older adult; oral health; periodontal disease; prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Keep Fit for Life: Meeting the Nutritional Needs of Older Persons. 2002. [(accessed on 30 May 2023)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42515.
-
- Petersen P.E., Kandelman D., Arpin S., Ogawa H. Global oral health of older people—Call for public health action. Community Dent. Health. 2010;27((Suppl. S2)):257–267. - PubMed
-
- World Report on Ageing and Health. 2015. [(accessed on 30 May 2023)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/186463.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources