Investigation of Crosslinking Parameters and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: From Design to Product Performances
- PMID: 37754414
- PMCID: PMC10530960
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9090733
Investigation of Crosslinking Parameters and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: From Design to Product Performances
Abstract
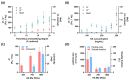
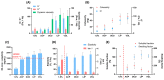
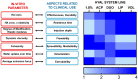
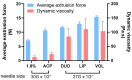
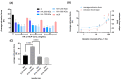
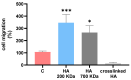
Despite process similarities, distinctive manufacturing technologies offer hyaluronic acid dermal fillers with different in vitro physicochemical and rheological properties due to peculiar crosslinked hydrogel networks. A better understanding of dermal filler properties could provide specific clinical indications and expectations with more accurate performance correlations. In this study, with an emphasis on the degree of modification, hyaluronic acid concentration and molecular weight, these process parameters were able to modulate dermal filler properties, especially rheology. Moreover, an extensive characterization of commercial hyaluronic acid injectables of the Hyal System line was described to present product properties and help to elucidate related clinical effects. Standardized methodologies were applied to correlate in vitro parameters with feasible clinical indications. In view of an optimized dermal filler design, the results of the extrudability measurements allowed the quantification of the effect of hydrogel composition, rheological properties and needle size on injectability. Composition, dynamic viscosity and needle size showed an impactful influence on hydrogel extrudability. Finally, the positive influence of 200 KDa hyaluronic acid in comparison to fragments of ether-crosslinked hyaluronic acid on fibroblast recognition were shown with a migration assay.
Keywords: crosslinking; dermal fillers; hyaluronic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
C.S. and A.F. declare no conflict of interest. S.P., A.M., A.D.L., D.G. and C.G. are currently employees of Fidia Farmaceutici S.p.A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Perspectives on the Injectability of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Standardized Methodology for Commercial Product Benchmarking with Inter-Injector Assessments.Gels. 2024 Jan 26;10(2):101. doi: 10.3390/gels10020101. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38391431 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Concepts in Rheology for the Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Soft Tissue Fillers.Dermatol Surg. 2021 May 1;47(5):e159-e167. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002916. Dermatol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33492870 Free PMC article.
-
Crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: a comparison of rheological properties.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008 Oct;87(1):264-71. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31675. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008. PMID: 18200557
-
The science of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers.J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008 Mar;10(1):35-42. doi: 10.1080/14764170701774901. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008. PMID: 18330796 Review.
-
The rheology of injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogels used as facial fillers: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 2):131880. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131880. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38677707 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Perspectives on the Injectability of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Standardized Methodology for Commercial Product Benchmarking with Inter-Injector Assessments.Gels. 2024 Jan 26;10(2):101. doi: 10.3390/gels10020101. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38391431 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating the Dilutional Rheology of Radiesse, Radiesse (+), and Radiesse With 0.26 mL of Lidocaine.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jan;24(1):e16649. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16649. Epub 2024 Oct 26. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39460517 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dual Functionalization of Hyaluronan Dermal Fillers with Vitamin B3: Efficient Combination of Bio-Stimulation Properties with Hydrogel System Resilience Enhancement.Gels. 2024 May 24;10(6):361. doi: 10.3390/gels10060361. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38920908 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation of Injectability Attributes in OxiFree™ Dermal Fillers: MaiLi® Product Variants and Clinical Case Reports.Gels. 2024 Apr 19;10(4):276. doi: 10.3390/gels10040276. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667695 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Dispersion Process to Improve Quality of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinked with 1,4-Butanediol Diglycidyl Ether.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;16(23):3323. doi: 10.3390/polym16233323. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ISAPS International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures. International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery; Mount Royal, NJ, USA: 2021. pp. 1–57.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

