Flaxseed Gum/Arabic Gum/Tween 80-Based Oleogel as a Fat Substitute Applied in Emulsified Sausage: Physicochemical Properties, Sensory Attributes and Nutritional Quality
- PMID: 37754440
- PMCID: PMC10530567
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9090759
Flaxseed Gum/Arabic Gum/Tween 80-Based Oleogel as a Fat Substitute Applied in Emulsified Sausage: Physicochemical Properties, Sensory Attributes and Nutritional Quality
Abstract
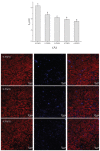
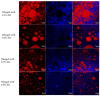
In the present study, flaxseed gum (FG), Arabic gum (GA) and Tween 80 were used to prepare oleogels through an emulsion-templated method, and the obtained oleogels were designed for the partial substitution of pork fat in emulsified sausage. An increment in FG concentrations enhanced the viscoelasticity of emulsions, which resulted in the improved stability of emulsion systems, with smaller droplet sizes. In addition, increased FG concentrations contributed to higher mechanical strength, denser network structure and lower oil loss of oleogels. As a fat substitute, the prepared oleogels improved the textural properties and nutritional quality of emulsified sausages. With the increase in the substitution level of oleogels, the hardness and chewiness of the emulsified sausage increased, and the cooking loss decreased. Meanwhile, the reformulation with oleogels decreased the saturated fat from 57.04 g/100 g lipid to 12.05 g/100 g lipid, while increasing the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 essential fatty acids from 0.10 to 0.39. The obtained results demonstrated that the flaxseed gum/Arabic gum/Tween 80-based oleogels had huge potential to successfully replace pork fat in emulsified sausage products.
Keywords: emulsified sausage; fat replacers; flaxseed gum; oleogels; rheological properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Bascuas S., Morell P., Hernando I., Quiles A. Recent trends in oil structuring using hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021;118:106612. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106612. - DOI
-
- Bolger Z., Brunton N.P., Monahan F.J. Impact of inclusion of flaxseed oil (pre-emulsified or encapsulated) on the physical characteristics of chicken sausages. J. Food Eng. 2018;230:39–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.02.026. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

