Effects of Sucrose Feeding on the Quality of Royal Jelly Produced by Honeybee Apis mellifera L
- PMID: 37754710
- PMCID: PMC10532100
- DOI: 10.3390/insects14090742
Effects of Sucrose Feeding on the Quality of Royal Jelly Produced by Honeybee Apis mellifera L
Abstract
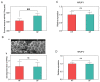
Royal jelly (RJ) is a highly nutritious secretion of the honeybees' hypopharyngeal glands (HPGs). During RJ production, colonies are occasionally subjected to manual interventions, such as sucrose feeding for energy supplementation. This study aimed to assess the impact of sucrose feeding on the composition of RJ. The results indicated that RJ obtained from sucrose-fed colonies exhibited significantly higher levels of fructose, alanine, glycine, tyrosine, valine, and isoleucine compared to the honey-fed group. However, no significant differences were observed in terms of moisture content, crude protein, 10-HDA, glucose, sucrose, minerals, or other amino acids within the RJ samples. Moreover, sucrose feeding did not have a significant effect on midgut sucrase activity, HPGs development, or the expression levels of MRJP1 and MRJP3 in nurse bees. Unsealed stored food samples from sucrose-fed bee colonies demonstrated significantly higher sucrose levels compared to sealed combs and natural honey. Additionally, natural honey exhibited higher moisture and Ca levels, as well as lower levels of Zn and Cu, in comparison to honey collected from bee colonies fed sucrose solutions. Based on these findings, we conclude that sucrose feeding has only a minor impact on the major components of RJ.
Keywords: Apis mellifera L.; nutritional compositions; royal jelly; stored food; sucrose feeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nagai T., Sakai M., Inoue R., Inoue H., Suzuki N. Antioxidative activities of some commercially honeys, royal jelly, and propolis. Food Chem. 2001;75:237–240. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00193-5. - DOI
-
- Ramadan M.F., Al-Ghamdi A. Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of royal jelly: A review. J. Funct. Foods. 2012;4:39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.12.007. - DOI
-
- Sabatini A.G., Marcazzan G.L., Caboni M.F., Bogdanov S., Almeida-Muradian L.B.D. Quality and standardisation of royal jelly. J. ApiProduct ApiMedical Sci. 2009;1:16–21. doi: 10.3896/IBRA.4.01.1.04. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 31702195/National Natural Science Foundation
- LJNY202003/the Efficient Ecological Agriculture Innovation Project of the Taishan Industry Leading Talent Program
- CARS-44/the earmarked fund for the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- ZR2022MC069/the Shandong Province National Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

