ST-Segment Elevation: An Unexpected Culprit
- PMID: 37754803
- PMCID: PMC10532326
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10090374
ST-Segment Elevation: An Unexpected Culprit
Abstract
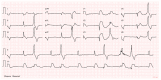
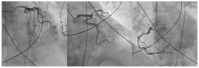
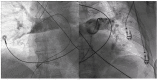
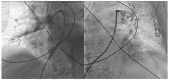
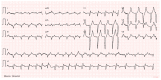
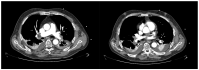
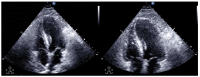
The clinical presentation of pulmonary embolism (PE) and acute coronary syndrome can be similar. We report a case of a patient presenting with antero-septal ST-segment elevation after cardiac arrest, found to have acute-PE-mimicking ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), treated with aspiration thrombectomy and catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT). A 78-year-old man was admitted with dyspnea, chest pain and tachycardia. During evaluation, cardiac arrest in pulseless electrical activity was documented. Advanced life support was started immediately. ECG post-ROSC revealed ST-segment elevation in V1-V4 and aVR. Echocardiography showed normal left ventricular function but right ventricular (RV) dilation and severe dysfunction. The patient was in shock and was promptly referred to cardiac catheterization that excluded significant CAD. Due to the discordant ECG and echocardiogram findings, acute PE was suspected, and immediate invasive pulmonary angiography revealed bilateral massive pulmonary embolism. Successful aspiration thrombectomy was performed followed by local alteplase infusion. At the end of the procedure, mPAP was reduced and blood pressure normalized allowing withdrawal of vasopressor support. Twenty-four-hour echocardiographic reassessment showed normal-sized cardiac chambers with preserved biventricular systolic function. Bedside echocardiography in patients with ST-segment elevation post-ROSC is instrumental in raising the suspicion of acute PE. In the absence of a culprit coronary lesion, prompt pulmonary angiography should be considered if immediately feasible. In these cases, CDT and aspiration in high-risk acute PE seem safe and effective in relieving obstructive shock and restoring hemodynamics.
Keywords: ST-segment; acute pulmonary embolism; aspiration thrombectomy; catheter-directed therapy; intervention cardiology; thrombolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pollack C.V., Schreiber D., Goldhaber S.Z., Slattery D., Fanikos J., O’Neil B.J., Thompson J.R., Hiestand B., Briese B.A., Pendleton R.C., et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: Initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011;57:700–706. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.071. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Konstantinides S.V., Meyer G., Becattini C., Bueno H., Geersing G.J., Harjola V.-P., Huisman M.V., Humbert M., Jennings C.S., Jiménez D., et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Eur. Heart J. 2020;41:543–603. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz405. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ibanez B., James S., Agewall S., Antunes M.J., Bucciarelli-Ducci C., Bueno H., Caforio A.L.P., Crea F., Goudevenos J.A., Halvorsen S., et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2018;39:119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

