Transport and Anaesthesia Consideration for Transcatheter Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Premature Infants
- PMID: 37754806
- PMCID: PMC10531776
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10090377
Transport and Anaesthesia Consideration for Transcatheter Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Premature Infants
Abstract
Transcatheter device closure of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in preterm infants has been proven to be a feasible and safe technique with promising results when compared to surgical ligation. However, managing transport and anaesthesia in extremely premature infants with haemodynamically significant PDA and limited reserves presents unique challenges. This review article focuses on the key considerations throughout the clinical pathway for the PDA device closure, including referral hospital consultation, patient selection, intra- and inter-hospital transport, and anaesthesia management. The key elements encompass comprehensive patient assessment, meticulous airway management, optimised ventilation strategies, precise thermoregulation, patient-tailored sedation protocols, vigilant haemodynamic monitoring, and safe transport measures throughout the pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative phases. A multidisciplinary approach enhances the chances of procedure success, improves patient outcomes, and minimises the risk of complications.
Keywords: anaesthesia; closure; devices; patent ductus arteriosus; premature babies; surgery; transcatheter; transcatheter PDA closure (TCPC); transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Belinda Chan has received consultant honoraria from the company GE, and 123 sonography. The other authors declare no financial interest.
Figures


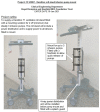




References
-
- Kuntz M.T., Staffa S.J., Graham D., Faraoni D., Levy P., DiNardo J., Maschietto N., Nasr V.G. Trend and Outcomes for Surgical Versus Transcatheter Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Neonates and Infants at US Children’s Hospitals. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022;11:e022776. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022776. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

