Mediating Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Associations between Physical Activity and Physical Fitness; Cross-Sectional Study among High School Adolescents
- PMID: 37754964
- PMCID: PMC10531934
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk8030131
Mediating Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Associations between Physical Activity and Physical Fitness; Cross-Sectional Study among High School Adolescents
Abstract
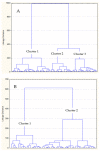
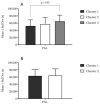
The COVID-19 pandemic and the imposed social distancing measures caused negative changes in physical activity levels (PALs) and physical fitness (PF) among adolescents, but the potential mediating effect of the pandemic on the association between PAL and PF is unknown. This study aimed to evaluate gender-specific associations between objectively measured PAL and indices of PF among high school adolescents during the period of the COVID-19 pandemic. The participants were 150 adolescents (101 females) aged 14-18 years; their anthropometrics were evaluated, and they were tested on PF (cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF; beep test), power (broad jump), flexibility (sit-and-reach test), and abdominal strength (sit-ups)) and PAL (using a pedometer for 7 days) during the pandemic period. A T-test was calculated to determine differences between genders. Associations between variables were evaluated using Pearson correlations. Additionally, multivariate taxonomic classification was used to sort participants into homogenous groups (clusters) according to their PF, and then analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to differentiate them according to PAL. For the total sample, PAL was correlated with CRF only (R = 0.25, p < 0.05), while gender-stratified correlations showed that PAL was significantly associated with CRF among girls only (R = 0.29, p < 0.05), which was additionally confirmed with multivariate cluster analysis and subsequent ANOVA. No association between PAL and PF was found for boys. The relatively low association between PAL and PF is most likely related to the mediating effect of the change in life circumstances during the COVID-19 pandemic, and limited applicability of pedometers in evaluating high-intensity PAL. Further studies in other age groups and environments are warranted.
Keywords: clusters; disease outbreak; health habits; lifestyle medicine; youth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-related physical fitness, physical activity and its correlates among school going adolescents in hilly state in north India: a cross sectional survey.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17808-3. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38326821 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-School Sports Participation Is Positively Associated with Physical Literacy, but What about Physical Education? A Cross-Sectional Gender-Stratified Analysis during the COVID-19 Pandemic among High-School Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2022 May 20;9(5):753. doi: 10.3390/children9050753. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626930 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Factors Associated with Physical Activity in the Elderly: A Cross-Sectional Study during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Jan 17;14(1):62. doi: 10.3390/bs14010062. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247714 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective analysis of physical activity levels and associated fitness factors amid COVID-19 pandemic and social-distancing rules. A special focus on adolescents.Sci Sports. 2022 Apr;37(2):131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Sci Sports. 2022. PMID: 35153371 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Physical-Literacy-Based Online Education on Indices of Physical Fitness in High-School Adolescents: Intervention Study during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period.Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 8;10(10):1666. doi: 10.3390/children10101666. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sekulic D., Blazevic M., Gilic B., Kvesic I., Zenic N. Prospective Analysis of Levels and Correlates of Physical Activity during COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Rules of Social Distancing; Gender Specific Study among Adolescents from Southern Croatia. Sustainability. 2020;12:4072. doi: 10.3390/su12104072. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources