Global Gene Expression of Post-Senescent Telomerase-Negative ter1 Δ Strain of Ustilago maydis
- PMID: 37755003
- PMCID: PMC10532341
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9090896
Global Gene Expression of Post-Senescent Telomerase-Negative ter1 Δ Strain of Ustilago maydis
Abstract
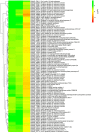
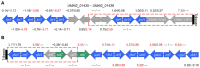
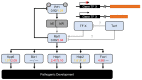
We analyzed the global expression patterns of telomerase-negative mutants from haploid cells of Ustilago maydis to identify the gene network required for cell survival in the absence of telomerase. Mutations in either of the telomerase core subunits (trt1 and ter1) of the dimorphic fungus U. maydis cause deficiencies in teliospore formation. We report the global transcriptome analysis of two ter1Δ survivor strains of U. maydis, revealing the deregulation of telomerase-deleted responses (TDR) genes, such as DNA-damage response, stress response, cell cycle, subtelomeric, and proximal telomere genes. Other differentially expressed genes (DEGs) found in the ter1Δ survivor strains were related to pathogenic lifestyle factors, plant-pathogen crosstalk, iron uptake, meiosis, and melanin synthesis. The two ter1Δ survivors were phenotypically comparable, yet DEGs were identified when comparing these strains. Our findings suggest that teliospore formation in U. maydis is controlled by key pathogenic lifestyle and meiosis genes.
Keywords: telomerase; ter1 mutants; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

