Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds from Edible Mushrooms to Attenuate SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Some Complications of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
- PMID: 37755005
- PMCID: PMC10532592
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9090897
Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds from Edible Mushrooms to Attenuate SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Some Complications of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
Abstract
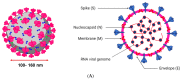
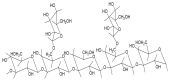
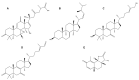
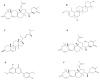
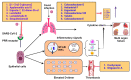
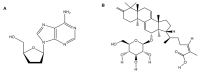
The novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a highly infectious positive RNA virus, has spread from its epicenter to other countries with increased mortality and morbidity. Its expansion has hampered humankind's social, economic, and health realms to a large extent. Globally, investigations are underway to understand the complex pathophysiology of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) induced by SARS-CoV-2. Though numerous therapeutic strategies have been introduced to combat COVID-19, none are fully proven or comprehensive, as several key issues and challenges remain unresolved. At present, natural products have gained significant momentum in treating metabolic disorders. Mushrooms have often proved to be the precursor of various therapeutic molecules or drug prototypes. The plentiful bioactive macromolecules in edible mushrooms, like polysaccharides, proteins, and other secondary metabolites (such as flavonoids, polyphenols, etc.), have been used to treat multiple diseases, including viral infections, by traditional healers and the medical fraternity. Some edible mushrooms with a high proportion of therapeutic molecules are known as medicinal mushrooms. In this review, an attempt has been made to highlight the exploration of bioactive molecules in mushrooms to combat the various pathophysiological complications of COVID-19. This review presents an in-depth and critical analysis of the current therapies against COVID-19 versus the potential of natural anti-infective, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antithrombotic products derived from a wide range of easily sourced mushrooms and their bioactive molecules.
Keywords: COVID-19 therapy; SARS-CoV-2; bioactive molecules anti-COVID-19; medicinal mushrooms; virus–host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Antiviral, Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Natural Medicinal Herbs and Mushrooms and SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 25;12(9):2573. doi: 10.3390/nu12092573. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32854262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico bioprospecting of antiviral compounds from marine fungi and mushroom for rapid development of nutraceuticals against SARS-CoV-2.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Mar;41(5):1574-1585. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.2023048. Epub 2021 Dec 31. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 34971338
-
Mechanistic Aspects of Medicinal Plants and Secondary Metabolites against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(38):3996-4007. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666210705160130. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 34225607 Review.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally Occurring Bioactives as Antivirals: Emphasis on Coronavirus Infection.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 29;12:575877. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.575877. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34267652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Seed: Phytochemical Profile, Bioactivity, and Nutraceutical Potential.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 16;13(6):e70390. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70390. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40524682 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Mushrooms as Multicomponent Mixtures-Demonstrated with the Example of Lentinula edodes.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;10(2):153. doi: 10.3390/jof10020153. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remedying SARS-CoV-2 through nature: a review highlighting the potentiality of herbs, trees, mushrooms, and endophytic microorganisms in controlling Coronavirus.Planta. 2025 Mar 16;261(4):89. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04647-8. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40089556 Review.
-
Quest for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antiviral therapeutics: in-silico and in-vitro analysis of edible mushroom- Cordyceps militaris.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024 May-Jun;15(3):100979. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2024.100979. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38871595 Free PMC article.
-
Is laccase from medicinal mushroom Cerrena unicolor cytotoxic to colon cancer cell line CT-26?PLoS One. 2025 May 8;20(5):e0322211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322211. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40338889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hadi A.G., Kadhom M., Hairunisa N., Yousif E., Mohammed S.A. A review on COVID-19: Origin, spread, symptoms, treatment, and prevention. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020;10:7234–7242.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

