The Preventive Mechanism of Anserine on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Liver Injury in L-02 Cells via Regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 and JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 37755089
- PMCID: PMC10532766
- DOI: 10.3390/md21090477
The Preventive Mechanism of Anserine on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Liver Injury in L-02 Cells via Regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 and JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
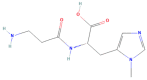
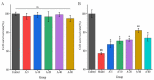
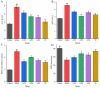
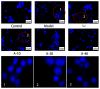
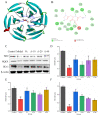
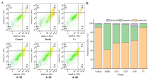
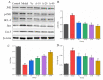
Anserine is a naturally occurring histidine dipeptide with significant antioxidant activities. This study aimed to investigate the preventive mechanism of anserine on tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP)-induced liver damage in a normal human liver cell line (L-02 cells). The L-02 cells were pretreated with anserine (10, 20, and 40 mmol/L) and then induced with 400 μmol/L of TBHP for 4 h. The results showed that the survival rates of L-02 cells and the contents of GSH were significantly increased with the pretreatment of anserine; the activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in the extracellular fluid were sharply decreased; and the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), nuclear fragmentation, and apoptosis were significantly inhibited. In addition, anserine could bind to the Kelch domain of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) with a binding force of -7.2 kcal/mol; the protein expressions of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2), quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and Bcl-2 were upregulated by anserine in TBHP-induced L-02 cells, with the downregulation of p-JNK and caspase-3. In conclusion, anserine might alleviated liver injury in L-02 cells via regulating related proteins in the Keap1-Nrf2 and JNK-Caspase-3 signaling pathways.
Keywords: JNK-Caspase-3; Keap1-Nrf2; L-02 cell; anrerine; apoptosis; liver injury; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

