Trash to Treasure: An Up-to-Date Understanding of the Valorization of Seafood By-Products, Targeting the Major Bioactive Compounds
- PMID: 37755098
- PMCID: PMC10532690
- DOI: 10.3390/md21090485
Trash to Treasure: An Up-to-Date Understanding of the Valorization of Seafood By-Products, Targeting the Major Bioactive Compounds
Abstract
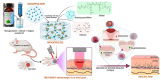
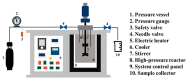
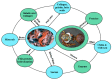
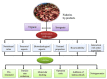
Fishery production is exponentially growing, and its by-products negatively impact industries' economic and environmental status. The large amount of bioactive micro- and macromolecules in fishery by-products, including lipids, proteins, peptides, amino acids, vitamins, carotenoids, enzymes, collagen, gelatin, chitin, chitosan, and fucoidan, need to be utilized through effective strategies and proper management. Due to the bioactive and healthy compounds in fishery discards, these components can be used as functional food ingredients. Fishery discards have inorganic or organic value to add to or implement in various sectors (such as the agriculture, medical, and pharmaceutical industries). However, the best use of these postharvest raw materials for human welfare remains unelucidated in the scientific community. This review article describes the most useful techniques and methods, such as obtaining proteins and peptides, fatty acids, enzymes, minerals, and carotenoids, as well as collagen, gelatin, and polysaccharides such as chitin-chitosan and fucoidan, to ensure the best use of fishery discards. Marine-derived bioactive compounds have biological activities, such as antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities. These high-value compounds are used in various industrial sectors, such as the food and cosmetic industries, owing to their unique functional and characteristic structures. This study aimed to determine the gap between misused fishery discards and their effects on the environment and create awareness for the complete valorization of fishery discards, targeting a sustainable world.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; circular economy; green extraction methodologies; seafood by-product; valorization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stankus A. FAO Aquaculture Newsletter. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2021. State of World Aquaculture 2020 and Regional Reviews: FAO Webinar Series; pp. 17–18.
-
- Roda M.A.P., Gilman E., Huntington T., Kennelly S.J., Suuronen P., Chaloupka M., Medley P. A Third Assessment of Global Marine Fisheries Discards. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2019.
-
- Ozogul F., Cagalj M., Šimat V., Ozogul Y., Tkaczewska J., Hassoun A., Kaddour A.A., Kuley E., Rathod N.B., Phadke G.G. Recent developments in valorisation of bioactive ingredients in discard/seafood processing by-products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;116:559–582. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.08.007. - DOI
-
- Haque A.R., Park J.-S., Ho T.C., Roy V.C., Ali M.S., Kiddane A.T., Kim G.-D., Chun B.-S. Characterization of oil and amino acids obtained from yellow corvina by-products using subcritical and supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2023;199:105970. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2023.105970. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

