The Impact of Transformational Leadership in the Nursing Work Environment and Patients' Outcomes: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37755351
- PMCID: PMC10537672
- DOI: 10.3390/nursrep13030108
The Impact of Transformational Leadership in the Nursing Work Environment and Patients' Outcomes: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: With the increasingly demanding healthcare environment, patient safety issues are only becoming more complex. This urges nursing leaders to adapt and master effective leadership; particularly, transformational leadership (TFL) is shown to scientifically be the most successfully recognized leadership style in healthcare, focusing on relationship building while putting followers in power and emphasizing values and vision.
Aim: To examine how transformational leadership affects nurses' job environment and nursing care provided to the patients and patients' outcomes.
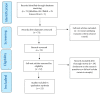
Design: A systematic literature review was conducted. From 71 reviewed, 23 studies were included (studies included questionnaire surveys and one interview, extracting barriers and facilitators, and analyzing using qualitative synthesis).
Result: TFL indirectly and directly positively affects nurses' work environment through mediators, including structural empowerment, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. Nurses perceived that managers' TFL behavior did not attain excellence in any of the included organizations, highlighting the necessity for additional leadership training to enhance the patient safety culture related to the non-reporting of errors and to mitigate the blame culture within the nursing environment.
Conclusion: Bringing more focus to leadership education in nursing can make future nursing leaders more effective, which will cultivate efficient teamwork, a quality nursing work environment, and, ultimately, safe and efficient patient outcomes. This study was not registered.
Keywords: nursing; systematic review; transformational leadership; work environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Panagioti M., Khan K., Keers R.N., Abuzour A.S., Phipps D., Kontopantelis E., Bower P., Campbell S., Haneef R., Avery A.J., et al. Prevalence, severity, and nature of preventable patient harm across medical care settings: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2019;366:l4185. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4185. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maben J., Conolly A., Abrams R., Rowland E., Harris R., Kelly D., Kent B., Couper K. “You can’t walk through water without getting wet” UK nurses’ distress and psychological health needs during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal in-terview study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2022;131:104242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104242. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials