Roles of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in diabetic myocardial microvascular injury
- PMID: 37755621
- PMCID: PMC10746668
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-023-01384-3
Roles of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in diabetic myocardial microvascular injury
Abstract
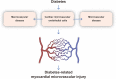
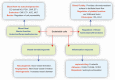
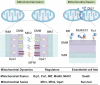
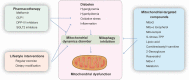
Myocardial microvessels are composed of a monolayer of endothelial cells, which play a crucial role in maintaining vascular barrier function, luminal latency, vascular tone, and myocardial perfusion. Endothelial dysfunction is a key factor in the development of cardiac microvascular injury and diabetic cardiomyopathy. In addition to their role in glucose oxidation and energy metabolism, mitochondria also participate in non-metabolic processes such as apoptosis, intracellular ion handling, and redox balancing. Mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy are responsible for regulating the quality and quantity of mitochondria in response to hyperglycemia. However, these endogenous homeostatic mechanisms can both preserve and/or disrupt non-metabolic mitochondrial functions during diabetic endothelial damage and cardiac microvascular injury. This review provides an overview of the molecular features and regulatory mechanisms of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Furthermore, we summarize findings from various investigations that suggest abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and defective mitophagy contribute to the development of diabetic endothelial dysfunction and myocardial microvascular injury. Finally, we discuss different therapeutic strategies aimed at improving endothelial homeostasis and cardiac microvascular function through the enhancement of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy.
Keywords: Cardiac microvascular injury; Diabetes; Endothelial cells; Mitochondrial dynamics; Mitophagy.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Cell Stress Society International.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in diabetic endothelial dysfunction and cardiac microvascular injury.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Dec;97(12):3023-3035. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03599-w. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37707623 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of coronary microvascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: focus on mitochondrial quality surveillance.Angiogenesis. 2022 Aug;25(3):307-329. doi: 10.1007/s10456-022-09835-8. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Angiogenesis. 2022. PMID: 35303170 Review.
-
Pathological Roles of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Cardiac Microvascular Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 5;10(1):85. doi: 10.3390/biom10010085. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31948043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NR4A1 aggravates the cardiac microvascular ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy and promoting Mff-required mitochondrial fission by CK2α.Basic Res Cardiol. 2018 May 9;113(4):23. doi: 10.1007/s00395-018-0682-1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2018. Retraction in: Basic Res Cardiol. 2023 Jun 15;118(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-00994-3. PMID: 29744594 Retracted.
-
L-carnitine alleviates cardiac microvascular dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy by enhancing PINK1-Parkin-dependent mitophagy through the CPT1a-PHB2-PARL pathways.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023 Jul;238(3):e13975. doi: 10.1111/apha.13975. Epub 2023 Apr 30. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 37042471
Cited by
-
GRK2 and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Cardiovascular Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 5;26(5):2299. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052299. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo1 deletion mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy by maintaining mitochondrial dynamics via ERK/Drp1 pathway.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 20;24(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02625-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40114130 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate affects myocardial vascular homeostasis by regulating the balance of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in the hearts of diabetic mice.J Int Med Res. 2025 Jun;53(6):3000605251346591. doi: 10.1177/03000605251346591. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40478179 Free PMC article.
-
BuyangHuanwu Decoction alleviates Endothelial Cell Apoptosis and Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction via Regulation of the MAPKK4/p38 Signaling Axis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Sep 23;21(13):2464-2479. doi: 10.7150/ijms.98183. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439466 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Endothelial Cells: A Key Driver of Organ Disorders and Aging.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;14(4):372. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040372. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

