Sources, Degradation, Ingestion and Effects of Microplastics on Humans: A Review
- PMID: 37755757
- PMCID: PMC10534390
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11090747
Sources, Degradation, Ingestion and Effects of Microplastics on Humans: A Review
Abstract
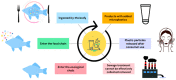
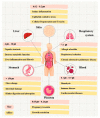
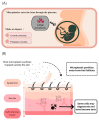
Celluloid, the predecessor to plastic, was synthesized in 1869, and due to technological advancements, plastic products appear to be ubiquitous in daily life. The massive production, rampant usage, and inadequate disposal of plastic products have led to severe environmental pollution. Consequently, reducing the employment of plastic has emerged as a pressing concern for governments globally. This review explores microplastics, including their origins, absorption, and harmful effects on the environment and humans. Several methods exist for breaking down plastics, including thermal, mechanical, light, catalytic, and biological processes. Despite these methods, microplastics (MPs, between 1 and 5 mm in size) continue to be produced during degradation. Acknowledging the significant threat that MPs pose to the environment and human health is imperative. This form of pollution is pervasive in the air and food and infiltrates our bodies through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. It is essential to assess the potential hazards that MPs can introduce. There is evidence suggesting that MPs may have negative impacts on different areas of human health. These include the respiratory, gastrointestinal, immune, nervous, and reproductive systems, the liver and organs, the skin, and even the placenta and placental barrier. It is encouraging to see that most of the countries have taken steps to regulate plastic particles. These measures aim to reduce plastic usage, which is essential today. At the same time, this review summarizes the degradation mechanism of plastics, their impact on human health, and plastic reduction policies worldwide. It provides valuable information for future research on MPs and regulatory development.
Keywords: environmental pollution; food chain; hazards; health; microplastics; plastics reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Bhuyan M.S. Effects of microplastics on fish and in human health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022;10:827289. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.827289. - DOI
-
- Wieland S., Balmes A., Bender J., Kitzinger J., Meyer F., Ramsperger A.F.R.M., Roeder F., Tengelmann C., Wimmer B.H., Laforsch C., et al. From properties to toxicity: Comparing microplastics to other airborne microparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022;428:128151. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Godara S.S., Yadav A., Goswami B., Rana R.S. Review on history and characterization of polymer composite materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2021;44:2674–2677. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.680. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

