ATM/Chk2 and ATR/Chk1 Pathways Respond to DNA Damage Induced by Movento® 240SC and Envidor® 240SC Keto-Enol Insecticides in the Germarium of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 37755764
- PMCID: PMC10535977
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11090754
ATM/Chk2 and ATR/Chk1 Pathways Respond to DNA Damage Induced by Movento® 240SC and Envidor® 240SC Keto-Enol Insecticides in the Germarium of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
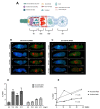
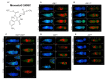
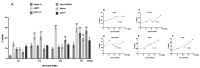
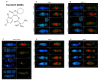
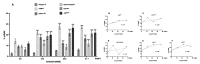
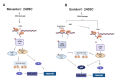
DNA damage response (DDR) pathways in keto-enol genotoxicity have not been characterized, and few studies have reported genotoxic effects in non-target organisms. The present study shows that concentrations of 11.2, 22.4, 37.3 mg/L of Movento® 240SC and 12.3, 24.6, 41.1 mg/L of Envidor® 240SC for 72 h oral exposure induced DSBs by significantly increasing the percentage of γH2AV expression in regions 2b and 3 from the germarium of wild type females of Drosophila melanogaster Oregon R, compared to the control group (0.0 mg/L of insecticides), via confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. The comparison between both insecticides' reveals that only the Envidor® 240SC induces concentration-dependent DNA damage, as well as structural changes in the germarium. We determined that the DDR induced by Movento® 240SC depends on the activation of the ATMtefu, Chk1grp and Chk2lok kinases by significantly increasing the percentage of expression of γH2AV in regions 2b and 3 of the germarium, and that ATRmei-29D and p53dp53 kinases only respond at the highest concentration of 37.3 mg/L of Movento® 240SC. With the Envidor® 240SC insecticide, we determined that the DDR depends on the activation of the ATRmei-29D/Chk1grp and ATMtefu/Chk2lok kinases, and p53dp53 by significantly increasing the percentage of expression of γH2AV in the germarium.
Keywords: DNA damage response; Drosophila germarium; keto-enol insecticides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologous checkpoint kinase Mei-41 induces a G2/M checkpoint in Drosophila imaginal tissue.Hereditas. 2018 Sep 6;155:27. doi: 10.1186/s41065-018-0066-4. eCollection 2018. Hereditas. 2018. PMID: 30202398 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM and Rad3-related protein exhibit selective target specificities in response to different forms of DNA damage.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 14;280(2):1186-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410873200. Epub 2004 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15533933
-
Lycopene inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced ATM/ATR-dependent DNA damage response in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Feb 1;52(3):607-615. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.010. Epub 2011 Nov 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22178412
-
The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2010;108:73-112. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380888-2.00003-0. Adv Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21034966 Review.
-
Predictive and Prognostic Value of DNA Damage Response Associated Kinases in Solid Tumors.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 3;10:581217. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.581217. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33224881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like Factor 4-Deficient Cells Are Sensitive to Etoposide-Induced DNA Damage.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 21;47(4):217. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040217. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gundogan K., Donmez-Altuntas H., Hamurcu Z., Akbudak I.H., Sungur M., Bitgen N., Baskol G., Bayram F. Evaluation of chromosomal DNA damage, cytotoxicity, cytostasis, oxidative DNA damage and their relationship with endocrine hormones in patients with acute organophosphate poisoning. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018;825:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2017.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hilgert Jacobsen-Pereira C., Dos Santos C.R., Troina Maraslis F., Pimentel L., Feijó A.J.L., Iomara Silva C., de Medeiros G.D.S., Costa Zeferino R., Curi Pedrosa R., Weidner Maluf S. Markers of genotoxicity and oxidative stress in farmers exposed to pesticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018;148:177–183. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nauen R., Bretschneider T., Elbert A., Fischer R., Tiemann R. Spirodiclofen and Spiromesifen. J. Pestic. Outlook. 2003;14:243–245. doi: 10.1039/b314855f. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

