Measuring Marine Biotoxins in a Hypersaline Coastal Lagoon
- PMID: 37755952
- PMCID: PMC10534363
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15090526
Measuring Marine Biotoxins in a Hypersaline Coastal Lagoon
Abstract
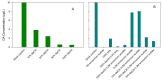
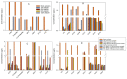
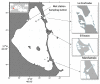
Marine biotoxins have posed a persistent problem along various coasts for many years. Coastal lagoons are ecosystems prone to phytoplankton blooms when altered by eutrophication. The Mar Menor is the largest hypersaline coastal lagoon in Europe. Sixteen marine toxins, including lipophilic toxins, yessotoxins, and domoic acid (DA), in seawater samples from the Mar Menor coastal lagoon were measured in one year. Only DA was detected in the range of 44.9-173.8 ng L-1. Environmental stressors and mechanisms controlling the presence of DA in the lagoon are discussed. As an enrichment and clean-up method, we employed solid phase extraction to filter and acidify 75 mL of the sample, followed by pre-concentration through a C18 SPE cartridge. The analytes were recovered in aqueous solutions and directly injected into the liquid chromatography system (LC-MS), which was equipped with a C18 column. The system operated in gradient mode, and we used tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) with a triple quadrupole (QqQ) in the multiple reaction monitoring mode (MRM) for analysis. The absence of matrix effects was checked and the limits of detection for most toxins were low, ranging from 0.05 to 91.2 ng L-1, depending on the compound. To validate the measurements, we performed recovery studies, falling in the range of 74-122%, with an intraday precision below 14.9% RSD.
Keywords: Mar Menor; coastal lagoons; liquid chromatography; marine toxins; solid phase extraction; triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Turner J.T., Tester P.A. Toxic marine phytoplankton, zooplankton grazers, and pelagic food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997;42:1203–1213. doi: 10.4319/lo.1997.42.5_part_2.1203. - DOI
-
- Doucette G., Maneiro I., Riveiro I., Svensen C. Ecological Studies. Volume 189. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2006. Phycotoxin Pathways in Aquatic Food Webs: Transfer, Accumulation and Degradation; pp. 283–295.
-
- Lefebvre K.A., Fachon E., Bowers E.K., Kimmel D.G., Snyder J.A., Stimmelmayr R., Grebmeier J.M., Kibler S., Ransom Hardison D., Anderson D.M., et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins in Alaskan Arctic food webs during the anomalously warm ocean conditions of 2019 and estimated toxin doses to Pacific walruses and bowhead whales. Harmful Algae. 2022;114:102205. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2022.102205. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

