Comparative Genomics of Staphylococcus rostri, an Undescribed Bacterium Isolated from Dairy Mastitis
- PMID: 37756052
- PMCID: PMC10534715
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci10090530
Comparative Genomics of Staphylococcus rostri, an Undescribed Bacterium Isolated from Dairy Mastitis
Abstract
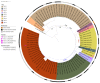
This study characterizes 81 S. rostri isolates from bovine mastitis (of which 80 were subclinical). The isolates were first identified as S. microti by MALDI-TOF MS, but later whole genome sequencing analysis allowed reclassification as S. rostri. The isolates were derived from 52 cows and nine dairy herds in Denmark. To describe the pathogenicity of S. rostri, we used whole genome sequencing to infer the distribution of genes associated with virulence, antibiotic resistance, and mobile genetic elements. Also, we performed a core-genome phylogeny analysis to study the genetic relatedness among the isolates. All 81 isolates expressed the same virulence profile comprising two putative virulence genes, clpP and clpC. Three isolates carried a resistance gene encoding streptomycin (str) or lincomycin (lnuA) resistance. The distribution of plasmids suggested the detected antibiotic resistance genes to be plasmid-mediated. Phages were abundant among the isolates, and the single isolate from clinical mastitis acquired a phage disparate from the rest, which potentially could be involved with virulence in S. rostri. The core genome phylogeny revealed a strong genetic intra-herd conservation, which indicates the source of introduction being herd-specific and might further imply the ability of S. rostri to adapt to the bovine niche and spread from cow-to-cow in a contagious manner. With this study, we aim to acquaint clinicians and professionals with the existence of S. rostri which might have been overlooked so far.
Keywords: Staphylococcus rostri; antibiotic resistance; bovine mastitis; non-aureus Staphylococci (NAS); phylogeny; virulence factors; whole genome-sequencing (WGS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An update on non-aureus staphylococci and mammaliicocci in cow milk: unveiling the presence of Staphylococcus borealis and Staphylococcus rostri by MALDI-TOF MS.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Aug;48(4):2555-2561. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10440-x. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38888631 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of non-aureus staphylococci from quarter milk, teat apices, and rectal feces of dairy cows, and their virulence potential.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Nov;103(11):10658-10675. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18265. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32921446
-
The diversities of staphylococcal species, virulence and antibiotic resistance genes in the subclinical mastitis milk from a single Chinese cow herd.Microb Pathog. 2015 Nov;88:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Microb Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26276706
-
Molecular epidemiology and distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes of Staphylococcus species isolated from Chinese dairy cows with clinical mastitis.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Feb;102(2):1571-1583. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15136. Epub 2018 Dec 24. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30591326
-
Non-aureus staphylococci in fecal samples of dairy cows: First report and phenotypic and genotypic characterization.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Oct;102(10):9345-9359. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16662. Epub 2019 Aug 14. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 31421888
Cited by
-
Mapping Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates from Subclinical Mastitis in Danish Dairy Cows.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 10;14(1):67. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010067. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858353 Free PMC article.
-
An update on non-aureus staphylococci and mammaliicocci in cow milk: unveiling the presence of Staphylococcus borealis and Staphylococcus rostri by MALDI-TOF MS.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Aug;48(4):2555-2561. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10440-x. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38888631 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

