Safety Assessment of an Oral Therapeutic Dose of Firocoxib on Healthy Horses
- PMID: 37756053
- PMCID: PMC10535825
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci10090531
Safety Assessment of an Oral Therapeutic Dose of Firocoxib on Healthy Horses
Abstract
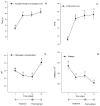
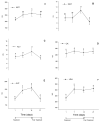
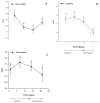
Firocoxib is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug specifically formulated for veterinary medicine and selectively acts on inhibiting the cyclooxygenase 2 enzyme (COX-2). This study evaluated the possible adverse effects of administering oral therapeutic firocoxib on gastric mucosa, hematological parameters, coagulation cascade, and hepatic and renal biochemistry in healthy horses. Nine clinically healthy Arabian horses, approximately 9 years old, received 0.1 mg/kg of oral firocoxib for 14 days. The gastroscopic examination was conducted 1 day before starting treatment (D0) and two days after the last blood collection (D23). Venous blood samples were obtained for laboratory tests on day 1, immediately prior to the initiation of treatment (D1), after 7 and 14 days of treatment (D7 and D14), and 7 days after the conclusion of treatment (D21. No changes were found in the gastroscopic and hematological tests. Coagulation and serum biochemistry levels remain between these species' average values. However, the increased activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and prothrombin time (PT) indicate reduced blood coagulation capacity, which contradicts the expected effect of treatment with selective COX-2 inhibitors, as these drugs theoretically promote coagulation. Administering firocoxib to horses is safe as it does not cause significant adverse reactions. Therefore, it is a suitable option for managing inflammatory conditions in these animals with attention to an unexpected adverse anti-coagulopathy effect, and further study is warranted.
Keywords: coagulation; drug safety; firocoxib; gastroscopy; hematology; selective COX-2 inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hematological and Biochemical Effects Associated with Prolonged Administration of the NSAID Firocoxib in Adult Healthy Horses.Vet Sci. 2024 Jun 5;11(6):256. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11060256. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38922003 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term administration of flunixin meglumine or firocoxib does not alter viscoelastic coagulation profiles in healthy horses.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2022 Oct 4;260(15):1963-1966. doi: 10.2460/javma.22.08.0367. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36198050
-
Effect of Firocoxib and Flunixin Meglumine on Large Colon Mural Thickness of Healthy Horses.J Equine Vet Sci. 2023 Jul;126:104562. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2023.104562. Epub 2023 May 11. J Equine Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37172749
-
Pharmacological Regulation in the USA and Pharmacokinetics Parameters of Firocoxib, a Highly Selective Cox-2, by Pain Management in Horses.J Equine Vet Sci. 2019 Jun;77:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2019.02.007. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Equine Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31133314 Review.
-
Update on the use of cyclooxygenase-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in horses.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2017 Jun 1;250(11):1271-1274. doi: 10.2460/javma.250.11.1271. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28509650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Firocoxib Use in Horses.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 May-Jun;39(3):e70117. doi: 10.1111/jvim.70117. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40317502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiorin E.V., Rodrigues N.N.P., Cota L.D.O., Seidel S.R.T., Barbosa A.P., Tokawa P.K.A. Clinical study of chondroitin sulfate urinary excretion following intramuscular application of the chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine association in horses. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec. 2023;75:355–359. doi: 10.1590/1678-4162-12839. - DOI
-
- Menzies-Gow N. Colic: Medical treatment and management in horses. Vet. Times. 2016;46:19–20.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

