Effect of the Probiotic Bacillus subtilis DE-CA9TM on Fecal Scores, Serum Oxidative Stress Markers and Fecal and Serum Metabolome in Healthy Dogs
- PMID: 37756088
- PMCID: PMC10537710
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci10090566
Effect of the Probiotic Bacillus subtilis DE-CA9TM on Fecal Scores, Serum Oxidative Stress Markers and Fecal and Serum Metabolome in Healthy Dogs
Abstract
Background: There is increasing interest in the use of Bacillus species as probiotics since their spore-forming ability favors their survival in the acidic gastric environment over other probiotic species. The subsequent germination of B. subtilis to their vegetative form allows for their growth in the small intestine and may increase their beneficial effect on the host. B. subtilis strains have also previously been shown to have beneficial effects in humans and production animals, however, no reports are available so far on their use in companion animals.
Study design: The goal of this study was therefore to investigate the daily administration of 1 × 109 cfu DE-CA9TM orally per day versus placebo on health parameters, fecal scores, fecal microbiome, fecal metabolomics, as well as serum metabolomics and oxidative stress markers in ten healthy Beagle dogs in a parallel, randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled design over a period of 45 days.
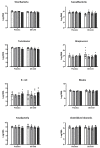
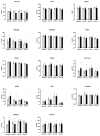
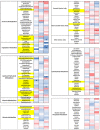
Results: DE-CA9TM decreased the oxidative status compared to controls for advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and reactive oxygen metabolites (d-ROMS), suggesting an antioxidant effect of the treatment. Fecal metabolomics revealed a significant reduction in metabolites associated with tryptophan metabolism in the DE-CA9TM-treated group. DE-CA9TM also significantly decreased phenylalanine and homocysteine and increased homoserine and threonine levels. Amino acid metabolism was also affected in the serum metabolome, with increased levels of urea and cadaverine, and reductions in N-acetylornithine in DE-CA9TM compared to controls. Similarly, changes in essential amino acids were observed, with a significant increase in tryptophan and lysine levels and a decrease in homocysteine. An increase in serum guanine and deoxyuridine was also detected, with a decrease in beta-alanine in the animals that ingested DE-CA9TM.
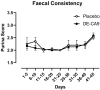
Conclusions: Data generated throughout this study suggest that the daily administration of 1 × 109 cfu of DE-CA9TM in healthy Beagle dogs is safe and does not affect markers of general health and fecal scores. Furthermore, DE-CA9TM administration had a potential positive effect on some serum markers of oxidative stress, and protein and lipid metabolism in serum and feces.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; metabolome; microbiome; oxidative stress; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential effect of two Bacillus probiotic strains on performance and fecal microbiota of breeding sows and their piglets.J Anim Sci. 2022 Jun 1;100(6):skac163. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac163. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35512239 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic effect of Bacillus subtilis B-2998D, B-3057D, and Bacillus licheniformis B-2999D complex on sheep and lambs.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2021 Mar 8;8(1):146-157. doi: 10.5455/javar.2021.h497. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2021. PMID: 33860025 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical study on sequential treatment of severe diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome with precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules, fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 28;12:1025889. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1025889. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36250045 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of metronidazole on the fecal microbiome and metabolome in healthy dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2020 Sep;34(5):1853-1866. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15871. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Vet Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32856349 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on fecal metabolome in rats after oral administration for 90 days].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Jun 18;52(3):457-463. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.010. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32541978 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of Bacillus subtilis ATCC PTA-122264 on apparent total tract macronutrient digestibility and fecal characteristics, metabolites, and microbiota of healthy adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf038. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf038. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 39923129
References
-
- Colom J., Freitas D., Simon A., Brodkorb A., Buckley M., Deaton J., Winger A.M. Presence and Germination of the Probiotic Bacillus subtilis DE111® in the Human Small Intestinal Tract: A Randomized, Crossover, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Study. Front. Microbiol. 2021;12:715863. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.715863. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lahiri K.R., Singh R., Apte M., Patil M., Taksande A., Varona R., Chatterjee G., Verma M., Brette S., Perez M.I. Efficacy and Safety of Bacillus Clausii (O/C, N/R, SIN, T) Probiotic Combined with Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) and Zinc in Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study in India. Trop. Dis. Travel. Med. Vaccines. 2022;8:9. doi: 10.1186/s40794-022-00166-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

