Lung extracellular matrix modulates KRT5+ basal cell activity in pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 37758700
- PMCID: PMC10533905
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41621-y
Lung extracellular matrix modulates KRT5+ basal cell activity in pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
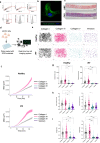
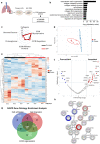
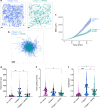
Aberrant expansion of KRT5+ basal cells in the distal lung accompanies progressive alveolar epithelial cell loss and tissue remodelling during fibrogenesis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The mechanisms determining activity of KRT5+ cells in IPF have not been delineated. Here, we reveal a potential mechanism by which KRT5+ cells migrate within the fibrotic lung, navigating regional differences in collagen topography. In vitro, KRT5+ cell migratory characteristics and expression of remodelling genes are modulated by extracellular matrix (ECM) composition and organisation. Mass spectrometry- based proteomics revealed compositional differences in ECM components secreted by primary human lung fibroblasts (HLF) from IPF patients compared to controls. Over-expression of ECM glycoprotein, Secreted Protein Acidic and Cysteine Rich (SPARC) in the IPF HLF matrix restricts KRT5+ cell migration in vitro. Together, our findings demonstrate how changes to the ECM in IPF directly influence KRT5+ cell behaviour and function contributing to remodelling events in the fibrotic niche.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.H. received, unrelated to the submitted work, consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim. P.L.M. received, unrelated to the submitted work, industry-academic funding from AstraZeneca via his institution and speaker and consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim Trevi and Hoffman-La Roche. A.J.B. received, unrelated to the submitted work, consultancy fees and/or industry/academic funding from Ammax, Devpro, and Ionis pharmaceuticals, via his institution. A.G.N. is or has been a scientific advisor relating to IPF trials for Medical Quantitative Image Analysis, Galapagos, Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche, as well as receiving payment for educational activities relating to interstitial lung disease from Boehringer Ingelheim and UpToDate. T.M.M. received, unrelated to the submitted work, consultancy fees in relation to pulmonary fibrosis from Abbvie, Agomab, Apellis, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Biogen Idec, Blade Therapeutics, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bridge Therapeutics, Carthronix, Chieisi, CohBar, CSLBehring, Daewoong, Daiatchi, DevPro, Endeavor, Fibrogen, Galapagos, Galecto, GlaxoSmithKline, Insilico, IQVIA, Kinevent, Pliant, Pfizer, Puretech, Qureight, Redx, Remedy Cell, Respivant Sciences, Roche, Shinogi, Surrozen, Theravance, Three Lakes Partners, Trevi, UCB, United Therapeutics, Veracyte, Vicore. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 203128/Z/16/Z /WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P89068 /DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 23983/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A31287 /CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A23983 /CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 104931/Z/14/Z /WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CDA 13-017/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CS-2013-13-017/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 202860/Z/16/Z /WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 107059/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/L015129/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

