Computer-aided diagnosis for screening of lower extremity lymphedema in pelvic computed tomography images using deep learning
- PMID: 37758908
- PMCID: PMC10533488
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-43503-1
Computer-aided diagnosis for screening of lower extremity lymphedema in pelvic computed tomography images using deep learning
Abstract
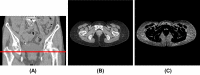
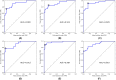
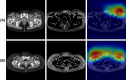
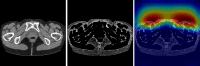
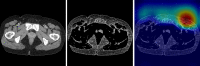
Lower extremity lymphedema (LEL) is a common complication after gynecological cancer treatment, which significantly reduces the quality of life. While early diagnosis and intervention can prevent severe complications, there is currently no consensus on the optimal screening strategy for postoperative LEL. In this study, we developed a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) software for LEL screening in pelvic computed tomography (CT) images using deep learning. A total of 431 pelvic CT scans from 154 gynecological cancer patients were used for this study. We employed ResNet-18, ResNet-34, and ResNet-50 models as the convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture. The input image for the CNN model used a single CT image at the greater trochanter level. Fat-enhanced images were created and used as input to improve classification performance. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to evaluate our method. The ResNet-34 model with fat-enhanced images achieved the highest area under the curve of 0.967 and an accuracy of 92.9%. Our CAD software enables LEL diagnosis from a single CT image, demonstrating the feasibility of LEL screening only on CT images after gynecologic cancer treatment. To increase the usefulness of our CAD software, we plan to validate it using external datasets.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

