Natural exosomes-like nanoparticles in mung bean sprouts possesses anti-diabetic effects via activation of PI3K/Akt/GLUT4/GSK-3β signaling pathway
- PMID: 37759297
- PMCID: PMC10536756
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-02120-w
Natural exosomes-like nanoparticles in mung bean sprouts possesses anti-diabetic effects via activation of PI3K/Akt/GLUT4/GSK-3β signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. Mung bean sprouts are traditionally considered a "folk" hypoglycemic food and their pharmacological effects and underlying mechanisms warrant further investigation.
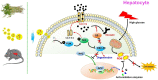
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the anti-diabetic effects of the exosomes-like nanoparticles in mung bean sprouts (MELNs) and explore the related molecular mechanisms.
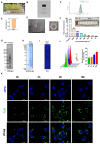
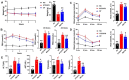
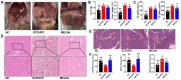
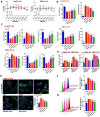
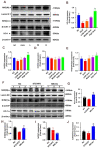
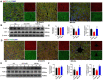
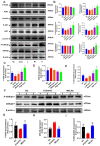
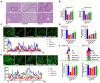
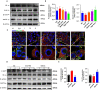
Results: MELNs were isolated using a differential centrifugation-polyethylene glycol (PEG) method, and the identification of MELNs were confirmed by PAGE gel electrophoresis, agarose gel electrophoresis, thin-layer chromatography (TLC), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). In the high-fat diet/streptozotocin (HFD/STZ) mouse model, MELNs ameliorated the progression of T2DM by increasing oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and insulin tolerance test (ITT) results, decreasing the fasting blood glucose level, and reducing the serum triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol (TC). Histopathological examinations indicated MELNs diminished inflammatory infiltration of hepatocytes and amplified the area of islet B cells. In addition, MELNs decreased the oxidative stress levels in liver tissue and had good biocompatibility. In vitro experiments verified that MELNs improved the viability of glucosamine (GlcN) induced insulin-resistant hepatocytes. Furthermore, this study also revealed that MELNs upregulated GLUT4 & Nrf2 and down-regulated GSK-3β via activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, promoting the production of antioxidant enzymes, such as HO-1 and SOD, to reduce oxidative stress.
Conclusion: MELNs mitigated the progression of type 2 diabetes in HFD/STZ mouse model. The underlying molecular mechanism is related to PI3K/Akt/GLUT4/GSK-3β signaling pathway.
Keywords: Exosome-like nanoparticles; Mung bean sprouts; Oxidative stress; Type 2 diabetes Mellitus.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MDG-1, a polysaccharide from Ophiopogon japonicus exerts hypoglycemic effects through the PI3K/Akt pathway in a diabetic KKAy mouse model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Aug 30;143(1):347-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.050. Epub 2012 Jul 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22776833
-
Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(10):839-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20150009. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201094
-
A novel formula Sang-Tong-Jian improves glycometabolism and ameliorates insulin resistance by activating PI3K/AKT pathway in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1585-1594. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.101. Epub 2016 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27829545
-
Trilobatin regulates glucose metabolism by ameliorating oxidative stress and insulin resistance in vivo and in vitro.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 3;77(2):236-248. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae035. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 38642915
-
A diarylheptanoid compound from Alpinia officinarum Hance ameliorates high glucose-induced insulin resistance by regulating PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-GSK3β signaling pathways in HepG2 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;295:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115397. Epub 2022 May 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35605918
Cited by
-
Medicinal Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles as Regulatory Mediators in Microenvironment for Disease Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 30;20:8451-8479. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S526287. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40620682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astragalus mongholicus polysaccharides alleviate insulin resistance through modulation of PI3K/AKT, TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway and microbiota in rats with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 May 24;15(3):274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.05.007. eCollection 2025 May. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40486274 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Omics Reveal Dendrobium nobile Lindl.'s Anti-Diabetic Mechanisms via Arginine/Proline and Glycerophospholipid Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;18(7):1061. doi: 10.3390/ph18071061. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732347 Free PMC article.
-
Diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates post-hepatectomy liver regeneration.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84403-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747625 Free PMC article.
-
Tangerine Peel-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles Alleviate Hepatic Steatosis Induced by Type 2 Diabetes: Evidenced by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Microflora.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 30;19:10023-10043. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S478589. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39371479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogurtsova K, Guariguata L, Barengo NC, Ruiz PL, Sacre JW, Karuranga S et al. IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021, Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022; 183:109118.10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109118. - PubMed
-
- Kazda CM, Ding Y, Kelly RP, Garhyan P, Shi C, Lim CN et al. Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of the Glucagon Receptor Antagonist LY2409021 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: 12- and 24-Week Phase 2 Studies, Diabetes Care 39(7) (2016) 1241 – 9.10.2337/dc15-1643. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS464/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

